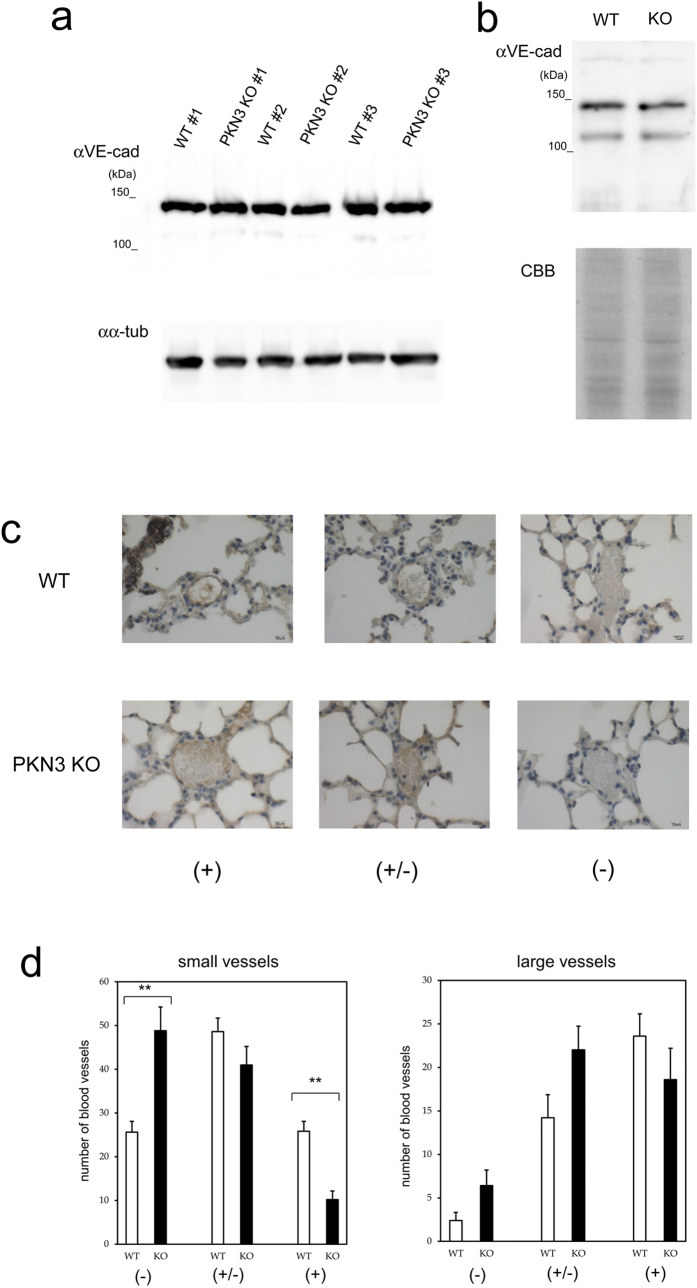
Figure 7. Expression of VE-cadherin in WT and PKN3 KO mouse lungs.
(a) Immunoblotting of the crude extract of mouse lungs with anti VE-cadherin antibody. Each crude extract of lung from individual WT mouse (#1 – #3) and PKN3 KO mouse (#1 – #3) was prepared by homogenizing lung directly with sample buffer for SDS-PAGE. “αVE-cad” and “αα-tub” indicate immunoblotting with anti VE-cadherin and anti α-tubulin antibodies, respectively. (b) Immunoblotting of the plasma membrane fraction of mouse lungs with anti VE-cadherin antibody. The plasma membrane fractions of mouse lungs were prepared using Minute Plasma Membrane Protein Isolation Kit (Invent Biotechnologies, Inc.). “αVE-cad” indicates immunoblotting with anti VE-cadherin antibody. “CBB” indicates Coomassie staining of the gel after SDS-PAGE. (c) Immunohistochemical staining of mouse lungs with anti VE-cadherin. Blood vessels were classified into dense (indicated by + ), moderate (indicated by +/−), and weak (indicated by −) immunoreactive staining groups. (−) indicates no immunoreactivity or indistinguishable from red blood cells. (+/−) indicates mild immunoreactivity detectable only at x 400 magnification. (+) indicates obvious immunoreactivity detectable even at x 100 magnification. (d) The number of blood vessels classified by the VE-cadherin immunoreactivity. Blood vessels were first classified into two groups by size (“small vessels” and “large vessels”), and further classified by VE-cadherin immunoreactivity as described in (C). “small vessels” indicate thin vessels in the peripheral in the intra or inter alveolar area. “large vessels” indicate thick vessels rich in tunica media along bronchus or vessels radiating from that thick vessel to periphery. “small vessels” were counted up to 100/each slice of lung, and all of the “large vessels” were counted in each slice. ** indicates P < 0.01.