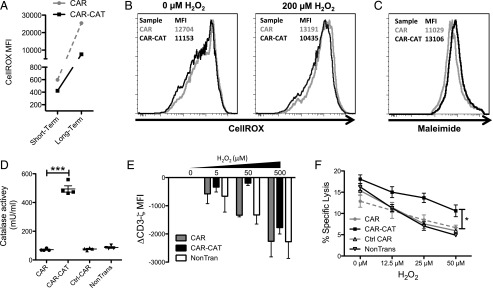
FIGURE 4.
A bystander effect is mediated by CAR-CAT T cells toward nonmodified T and NK cells. (A) T cells were labeled with CellROX for both a short-term and long-term staining, and CellROX MFI on CAR− T cells was determined after cells were acquired by FACS. (B) Healthy donor autologous T cells were CFSE labeled and admixed with transduced T cells followed by staining with Abs and CellROX and acquired by flow cytometry. (C) CAR-CAT and CAR− cells were labeled with maleimide and surface thiols were evaluated. (D) Supernatants were collected from transduced and nontransduced T cells and tested for catalase activity. (E) H2O2 was used to induce oxidative stress in T cell culture for 2 h prior to staining. Cells (2 × 105) were stained for CD3ζ using FITC-conjugated anti-CD3ζ after permeabilization with 0.25% PFA and digitonin. Cells were acquired by FACS, and change in CD3ζ MFI was calculated by: CD3ζ MFI(xμM H2O2) − CD3ζ MFI(0μM H2O2) gated on the CAR− fraction. (F) NK cells were cocultured with engineered T cells at a ratio of 2:1 CAR T cell/NK cell overnight under oxidative stress induced by different concentrations H2O2. K562 target cells were loaded with [51Cr] and added to the NK/T cell mix after H2O2 coculture at a ratio of 1:1 NK cell/K562 cell. Supernatant (25 μl) was transferred to LumaPlates and read out on MicroBeta. Data are presented as means ± SD. *p < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA using GraphPad Prism 5 for (C) between CAR and CAR-CAT.