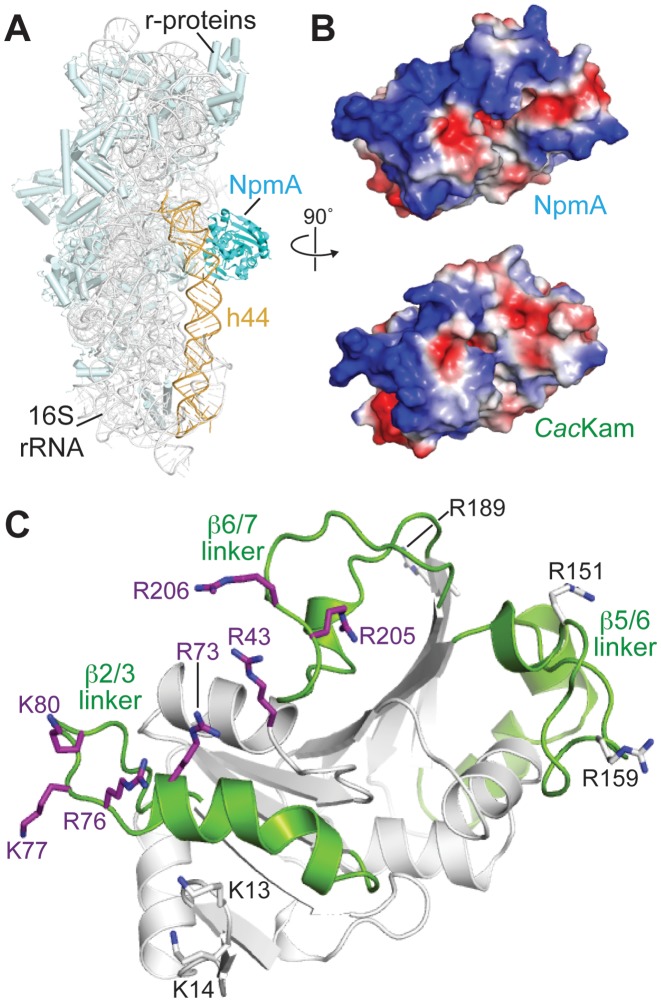
Figure 4.
CacKam residues that mediate interaction with 30S substrate. (A) Structure of the 30S-NpmA complex (4OX9) highlighting the enzyme binding site at the top of h44, within the decoding center. (B) Top, an orthogonal view of NpmA showing the 30S interaction surface in electrostatic potential representation. Regions of the most negative electrostatic potential are in red and most positive are in blue. Bottom, equivalent view and electrostatic surface potential of CacKam, produced by alignment of the apo CacKam structure with 30S-bound NpmA. (C) Cartoon of the CacKam structure in the same orientation as panel B, highlighting three regions (β2/3, β5/6, and β6/7 linkers) equivalent to those which mediate interaction of NpmA with 30S (18). Residues substituted to alanine (Table 2) are shown as sticks; those resulting in enzymes with reduced (MIC < 256 μg/ml) or comparable (MIC > 512 μg/ml) ability to confer resistance to kanamycin compared to the wild-type enzyme are colored purple and white, respectively.