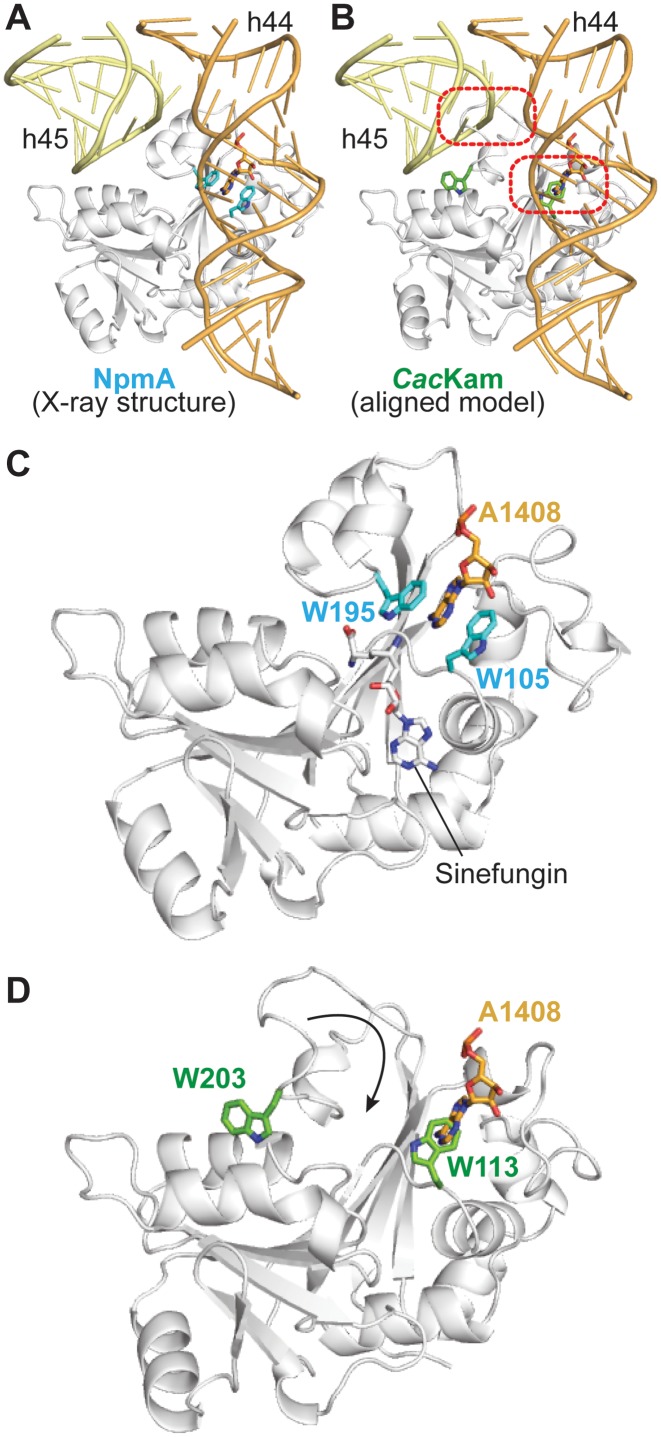
Figure 5.
Interaction with 30S requires remodeling of the CacKam β6/7 linker. (A) View of NpmA bound to the 16S rRNA surface formed by h44 and h45 (yellow and orange, respectively). The universally conserved pair of Trp residues and the A1408 target nucleotide are shown as sticks. (B) Equivalent view of a model of the CacKam-30S complex generated by alignment of CacKam to the 30S-bound NpmA structure. Two sites of clash between CacKam and 16S rRNA are highlighted (dashed red boxes): the CacKam β6/7 linker overlaps with h45 of 30S, and a rotation of W113 is also necessary to accommodate the A1408 base in the enzyme active site. Zoomed views showing only (C) NpmA and (D) CacKam in the same orientation. A movement of CacKam W203 of >10 Å is necessary to adopt an equivalent position to NpmA W195 for interaction with A1408.