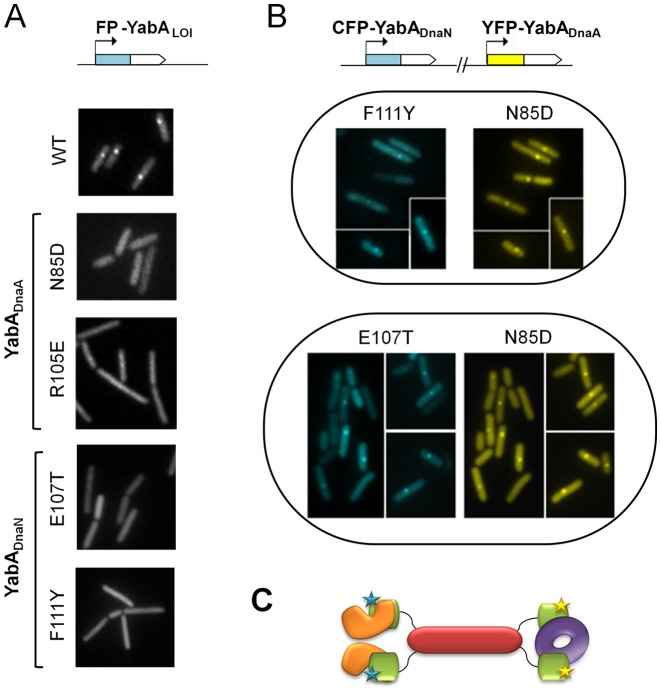
Figure 6.
Cellular localization of YabA-WT and -LOI mutants by fluorescence monitoring of signals from CFP- (cyan) or YFP- (yellow) YabA fusions in living cells. (A) Impaired localization of YabA LOI mutants in DnaA (N85D and R105E) and in DnaN (E107T and F111Y) compared to YabA-WT. (B) Restoration of localization of YabADnaN-LOI mutants by cross-complementation with a YabA-DnaA-LOI mutant. The co-expression in the same cell of the YabA-DnaN mutants F111Y or E107T fused to CFP (blue) with a YabA-DnaA N85D fused to YFP (yellow) restored the ability of each YabA mutant derivative to localize as a focus at the cell centre. The co-localization of foci indicates that they are part of a DnaA/YabA/DnaN complex, where the YabA tetramer is potentially composed of a mixture of YabA-DnaN (proficient for binding to DnaA) and YabA-DnaA (proficient for binding to DnaN) mutants. (C) Model illustrating cross complementation between YabA-DnaA (CTDs in green with yellow stars) and YabADnaN (CTDs in green with blue stars) for the binding and the cellular localization of DnaN (purple doughnut) and DnaA (orange). The YabA NTD's tetrameric core is represented in Indian red.