Figure 1.
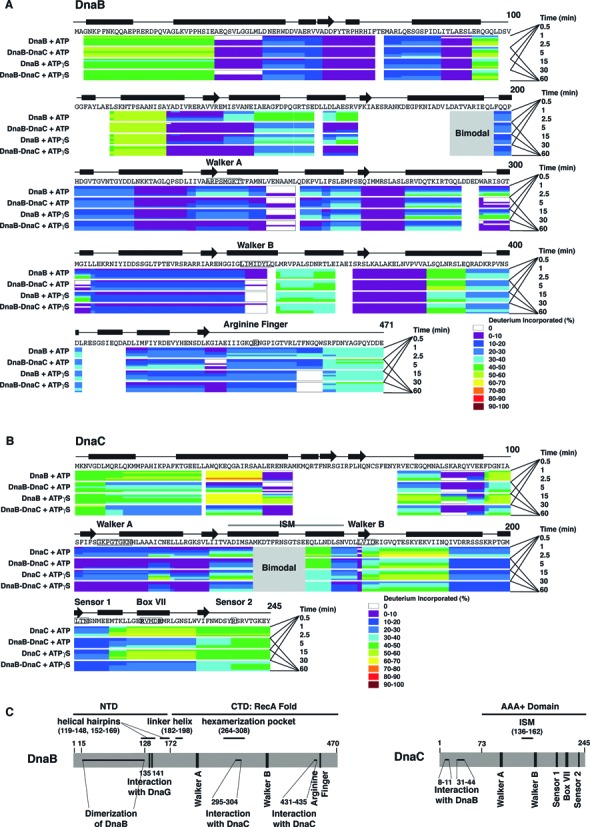
H/D exchange by peptides of DnaB and DnaC, color coded by percentage of deuterium exchanged. Deuteration of respective peptides of DnaB (panel A), DnaC (panel B) or the BC complex (panel A, B) in the presence of ATP or ATPγS was measured at the times indicated, and then the percentage of deuteration calculated (see Materials and Methods). The primary sequences of DnaB and DnaC, regions of secondary structure, the Walker A and B boxes, the arginine finger (arginine 442) of E. coli DnaB, and the initiator specific module (ISM) and AAA+ motifs of DnaC are also shown. The black bars and arrows represent α helices and β strands, respectively. In panel C, the N-terminal domain (NTD) of DnaB proposed to be involved in dimerization of DnaB (41–44), residues 135 and 141 required for interaction with primase (45,46), and its larger C-terminal domain (CTD) involved in nucleotide binding and hydrolysis and in interacting with DnaC (residues 295–304 and 431–435) correlate with the X-ray crystallographic structure of Geobacillus kaustophilus and Geobacillus stearothermophilus DnaB (8,10). The vertical bars represent the Walker A and B boxes and the arginine finger (arginine 442 of E. coli DnaB). Other functional domains shown are the helical hairpins (residue 119–148, 152–169), the linker helix (residue 182–198), and the domain that forms the hexamerization pocket (residue 264–308). For DnaC, its sites that interact with DnaB, the ISM, and the AAA+ motifs of its AAA+ domain are shown.
