FIGURE 6.
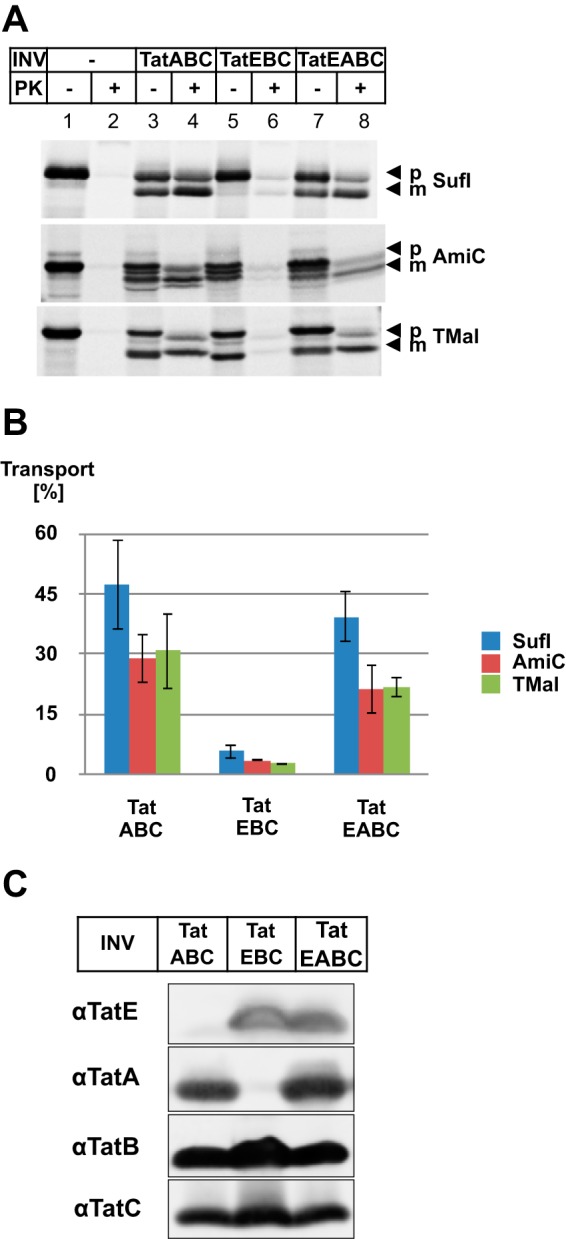
Influence of TatE on the translocation of in vitro-synthesized Tat-dependent substrates. A, the RR precursor proteins pSufI, TorA-MalE (TMal), and AmiC were in vitro-synthesized and radiolabeled by cell-free transcription/translation in the absence or presence of INV containing, in addition to TatB and TatC, either TatA (TatABC), TatE (TatEBC), or both (TatEABC). Where indicated, samples were digested with proteinase K (PK) to visualize protease-resistant, i.e. translocated, precursor (p) and mature (m) forms of the indicated proteins. Radiolabeled proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by phosphorimaging. B, quantitative data (mean ± S.E.) obtained from seven parallel experiments for the precursor protein pSufI (blue columns) and three parallel experiments for the precursors AmiC (red columns) and TorA-MalE (green columns) shown in A. Transport efficiency of the indicated INV was calculated using analyzing tools of ImageQuantTL. INV containing only TatEBC showed significantly reduced translocation activity compared with INV containing TatABC and TatEABC. C, the Tat components of the indicated vesicles were separated by Tricine SDS-PAGE and visualized by immunoblotting using polyclonal antibodies against TatE (αTatE), TatA (αTatA), TatB (αTatB), and TatC (αTatC).
