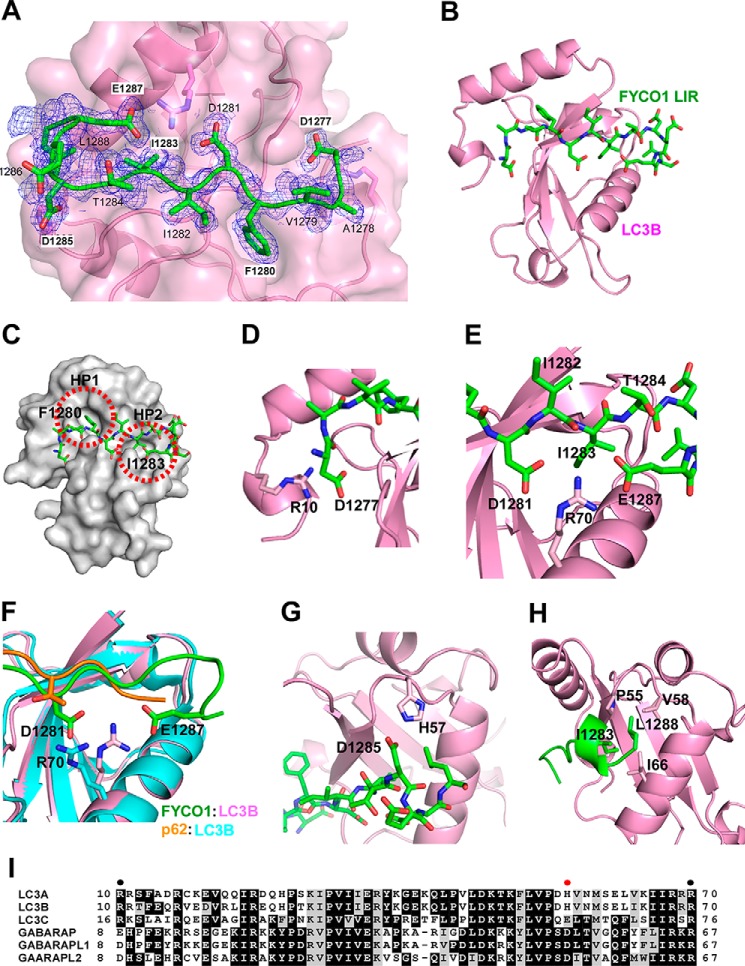
FIGURE 3.
Structure of FYCO1 LIR peptide bound to LC3B. A, electron density map of FYCO1 peptide on LC3. The Fo − Fc omit map of the FYCO1 peptide is contoured at 0.6 σ. B, overview of the LIR peptide (residues 1276–1288)(green) bound to LC3B (1–125)(magenta). Note that the structure in B is rotated 180 degrees relative to A. C, the side chains of the aromatic Phe1280 residue and the hydrophobic Ile1283 residues dock into hydrophobic pockets HP1 and HP2 of the LIR docking site of LC3B. D, detail of the electrostatic interaction between Arg10 in the N-terminal arm of LC3B and Asp1277 located N-terminal to the core LIR. E, both Glu1287 and Asp1281 of the LIR engage in electrostatic interactions with Arg70 of LC3B. F, this interaction involving Arg70 is not seen in the p62 LIR-LC3B complex as visualized in the structural comparison. G, the electrostatic interaction between FYCO1 Asp1285 and His57 in LC3B is likely a specificity determinant important for the preferential binding of FYCO1 to LC3A and -B. H, the most C-terminal Leu1288 residue in the crystalized LIR peptide engages in hydrophobic interactions with Pro55, Val58, and Ile66 of LC3B. I, sequence alignment of human ATG8 proteins generated with Clustal Omega (46). EPS image was generated with BOXSHADE. Shading indicates similarity. Solid circles indicate residues in LC3B required for interaction with FYCO1 LIR. Red solid circle indicates residue in LC3A/B conferring preference toward FYCO1 interaction.