FIGURE 4.
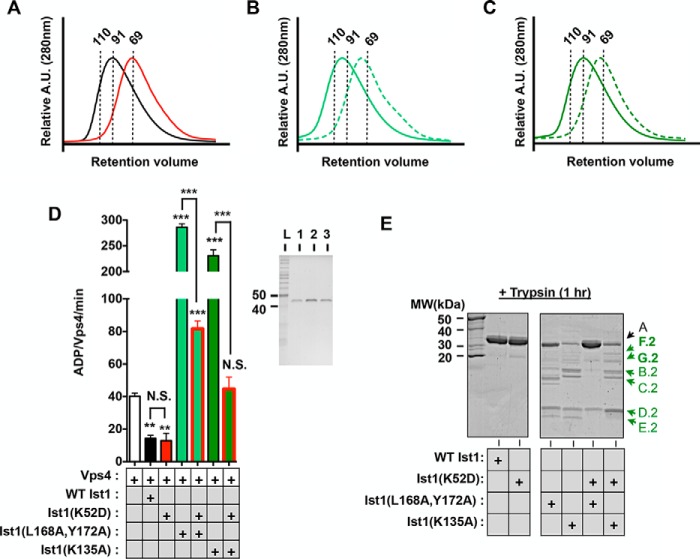
K52D stabilizes a more closed Ist1 conformation to prevent Vps4 hyperstimulation. A–C, UV traces for SEC analyses of Ist1: A, WT Ist1 (black) and Ist1(K52D) (red); B, Ist1(L168A,Y172A) (solid) and Ist1(L168A,Y172A,K52D) (dashed); C, Ist1(K135A) (solid) and Ist1(K135A,K52D) (dashed). A.U., absorption units. D, ATPase activities of 500 nm Vps4 in the presence of 8 μm Ist1 K52D mutants with or without L168A,Y172A and K135A. Results are presented as mean ± S.D. of triplicate experiments, with statistical differences from 500 nm Vps4 alone indicated (***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.005). The purity of recombinant Ist1 proteins as assessed by SDS-PAGE analysis and Coomassie staining is shown in the right panel. Lane 1, Ist1(K52D); lane 2, Ist1(L168A,Y172A, K52D); lane 3, Ist1(K135A, K52D). L, ladder; N.S., not significant. E, limited proteolysis of Ist1 with trypsin. Aliquots were removed at the 1-h time point for SDS-PAGE analysis and Coomassie staining. Additional peptide fragments in F.2 and G.2 are highlighted in the Ist1(K135A,K52D) sample. MW, molecular weight.