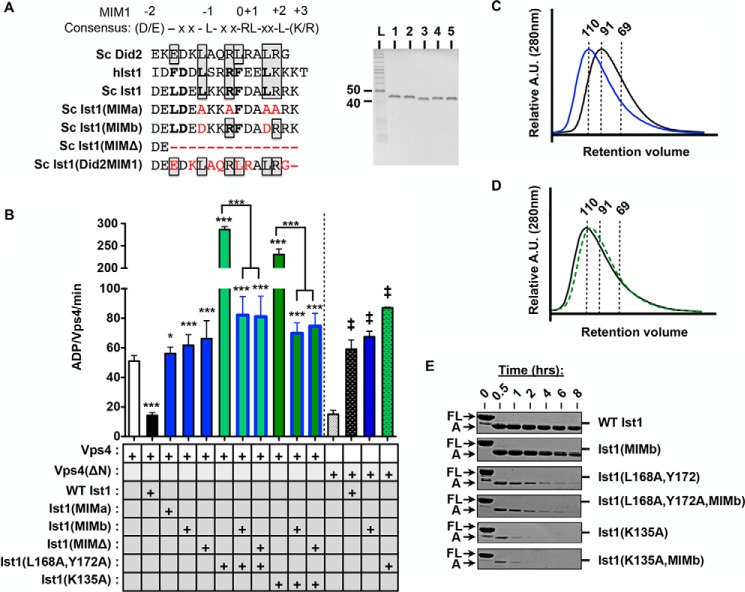
FIGURE 5.
Disrupting the Ist1 MIM-Vps4 MIT interaction results in loss of Vps4 inhibition and hyperstimulation. A, sequence alignment of α6 of yeast (Sc) Ist1, human (h) Ist1, and Sc Did2. MIM1 residues are boxed, and MIM3 residues are bold. Some residues contribute to both MIM1 and MIM3 modes of interaction (33). Residues mutated in the Ist1 MIM mutants used in this study are highlighted in red. The purity of recombinant Ist1 proteins as assessed by SDS-PAGE analysis and Coomassie staining is shown in the right panel. Lane 1, Ist1(MIMa); lane 2, Ist1(MIMb); lane 3, Ist1(MIMΔ); lane 4, Ist1(L168A,Y172A,MIMb); lane 5, Ist1(K135A,MIMb). L, ladder. B, ATPase activity of 500 nm Vps4 or Vps4(ΔN) in the presence of 8 μm Ist1 MIM mutants. Results are presented as mean ± S.D. of triplicate experiments, with statistical differences from 500 nm Vps4 alone indicated (*, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001) of Vps4(ΔN) alone (‡, <0.001). C and D, UV traces for SEC analyses of Ist1: C, WT Ist1 (black) and Ist1(MIMb) (blue); D, Ist1(L168A,Y172A,MIMb (black) and Isg1(K135A,MIMb) (green, dashed). A.U., absorption units. E, limited proteolysis of Ist1 with trypsin. Aliquots were removed at various time points for SDS-PAGE analysis and Coomassie staining. Full-length (FL) Ist1 and the A fragments are indicated.