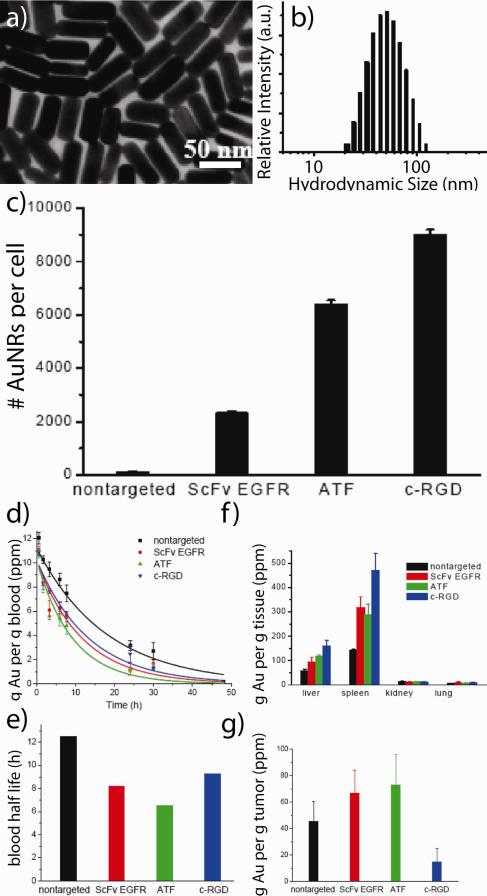
Figure 4. Effects of active targeting on the in vitro uptake and in vivo pharmacokinetics/biodistribution of anticancer gold nanorods.
(a) Electron micrographs of near-infrared absorbing colloidal gold nanorods and (b) their corresponding distribution of hydrodynamic diameters. (c) Enhanced in vitro binding/uptake of actively targeted gold nanorods as determined by mass spectrometry (ICP). In vitro accumulation of single-chain variable fragment (ScFv), peptide fragment (ATF), and cyclic cell-penetrating peptide (c-RGD) targeted nanorods was significantly enhanced. In contrast, in vivo (d) pharmacokinetics, (e) blood half-lives, (f) biodistribution, and (g) tumor-specific accumulation was only marginally enhanced. Adapted with permission from Ref. 24. Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society.