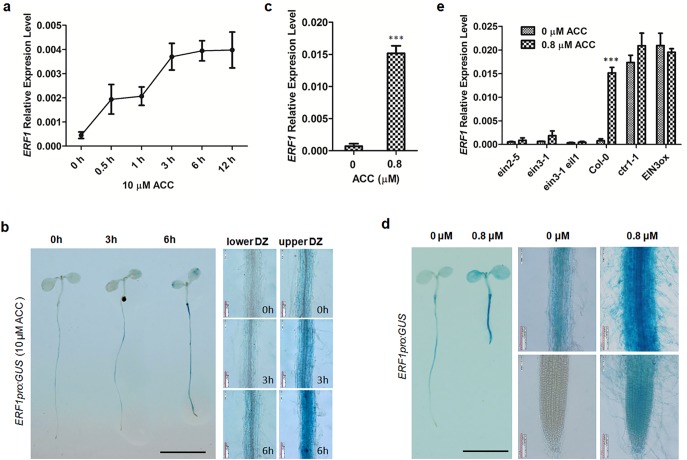
Fig 1. ERF1 expression is responsive to ethylene.
(a) Ethylene-induced ERF1 expression in wildtype. Seeds of Col-0 were germinated on MS medium for 5 d then treated with 10 μM ACC for 0, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, and 12 h. The transcriptional level of ERF1 was detected by quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). Values are mean ± SD of three replicates. ACC, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (precursor of ethylene biosynthesis). (b) Ethylene-induced expression of ERF1pro:GUS. Five-day-old seedlings of transgenic lines of were treated with 10 μM ACC for 0, 3, and 6 h before GUS staining. Upper DZ and lower DZ represent different primary root regions. Scale bar, 0.5 cm. (c) Ethylene-induced expression of ERF1 in wildtype. Seeds of Col-0 were germinated on MS medium with 0 or 0.8 μM ACC for 5 d, and relative ERF1 transcription levels measured by qRT-PCR. Values are mean ± SD of three replicates (***P<0.001). Asterisks indicate Student’s t-test significant differences. (d) Ethylene-activated expression in ERF1pro:GUS lines. Transgenic plants were grown MS medium with either 0 or 0.8 μM ACC for 5 d before GUS staining assay. Scale bar, 0.5 cm. (e) The relative ERF1 expression level was determined in ethylene signaling related mutants ein2-5, ein3-1, ein3-1eil1and compared to wildtype (Col-0) seedlings. Seedlings carrying constructs for either constitutive (ctr1-1) or inducible EIN3-FLAG (iE/qm) (EIN3ox) expression were also examined. Seedlings were geminated on MS medium with either 0 or 0.8 μM ACC for 5 d. Seeds of EIN3ox were grown on medium containing 1 μM β-estradiol and 0 or 0.8 μM ACC. Roots of seedlings were used for qRT-PCR analysis. Values are mean ± SD of three replicas (***P<0.001). Asterisks indicate Student’s t-test significant differences.