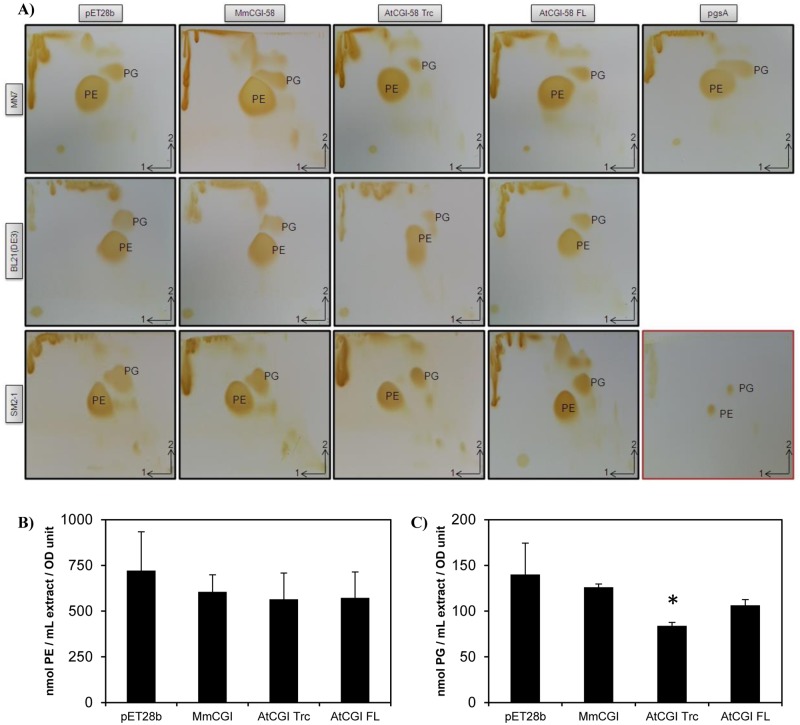
Fig 4. Analysis of phospholipids extracted from strains transformed with different versions of CGI-58.
Strain MN7 deficient in PG synthesis [20], wt strain BL21(DE3) and strain SM2-1 deficient in PA synthesis [21] were all transformed with either the void plasmid, the CGI-58 from mouse, or the full-length or truncated version from plant CGI-58. pgsA was also used as a positive control to restore PG synthesis in MN7. MN7 and SM2-1 strains had been previously transformed with pYAT7. A) TLC analysis of total lipids extracted after a 4 h-induction of transformants by 1 mM IPTG, then separated by 2-D TLC with, first, chloroform/methanol/water (65:25:4, v/v/v), and then with chloroform/methanol/acetic acid (65:25:10, v/v/v). After drying the plates, the lipids were visualized by exposure to diiodine vapor. TLC with authentic PE and PG standards is shown in the bottom right-hand corner (red frame). Each experiment was repeated at least thrice. B) Measurement of PE content of SM2-1 transformants determined by LC/MS/MS. Total lipids were extracted as above and analyzed. The quantities of PE were calculated based on a 36:2 PE standard curve and normalized with the OD600nm values of the liquid cultures after a 4 h-induction by IPTG. Values ± SD are the mean of three independent clones. C) PG content in SM2-1 transformants determined by LC/MS/MS. Total lipids were extracted as above and analyzed. The quantities of PG were calculated based on a 28:0 PG standard curve and normalized with the OD values as above. Values ± SD are the mean of three independent clones. * P<0.05, (vs pET28b).