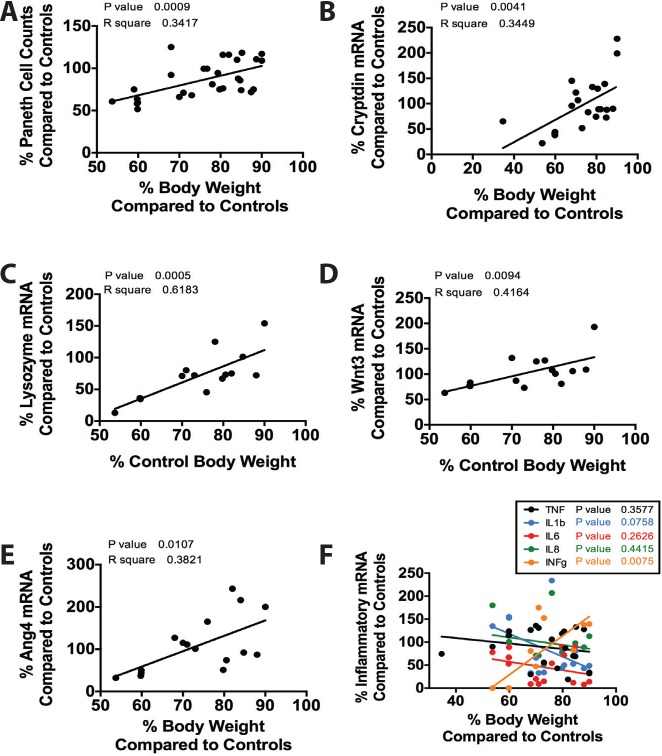
Fig 7. The severity of IUGR significantly impacts its effect on Paneth cells.
Data obtained from prior experiments were calculated as a percentage of change from the average control value of the same age. Data were plotted as deviation in weight compared to change in the desired variable and significance was determined using linear regression. There was a significant correlation between severity of IUGR and (A) Paneth cell loss (n = 29, p = 0.0009, r2 = .34), (B) decrease in cryptdin mRNA expression (n = 22, p = 0.0041, r2 = .34), (C) decrease in lysozyme mRNA (n = 15, p = 0.0005, r2 = 0.62), (D) decrease in Wnt3 mRNA (n = 15, p = 0.0094, r2 = 0.42), (E) decrease in Ang4 mRNA (n16, p = 0.012, r2 = 0.38), (F) and decrease in INF-γ mRNA (n = 15, p = 0.0075, r2 = 0.56). (F) While statistically non-significant, there were trends towards increased mRNA levels of TNF, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8, which are all pro-inflammatory cytokines seen in inflammatory intestinal diseases.