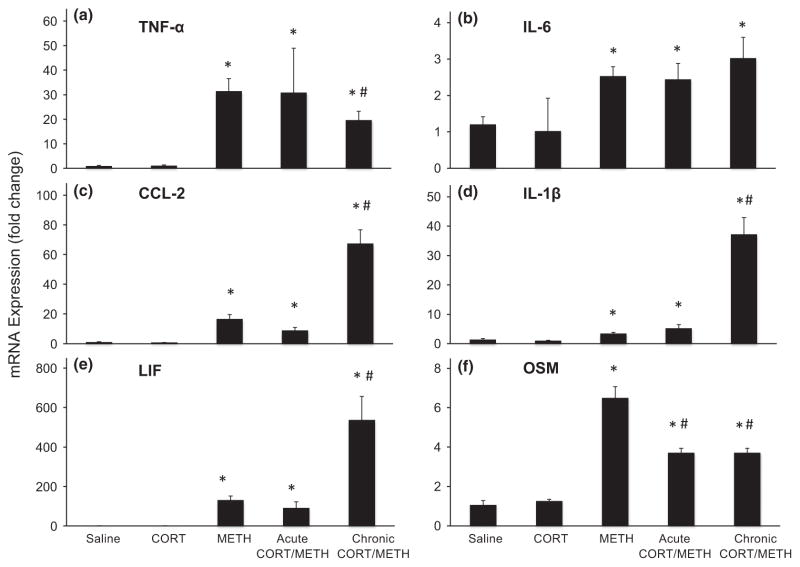
Fig. 1.
Chronic corticosterone (CORT) enhances methamphetamine (METH)-induced expression of some proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines in striatum. Acute CORT (20 mg/kg, s.c.) was administered 30 min prior to METH (20 mg/kg, s.c.), and chronic CORT (400 mg/L in 1.2% EtOH) was administered for 1 week in the drinking water prior to METH (20 mg/kg, s.c.) or corresponding saline (0.9%, s.c.) controls. At 12 h post METH or saline injection, mice were killed and total RNA was extracted from the striatum. Real-time PCR analysis was performed for TNF-α (a), IL-6 (b), CCL-2 (c), IL-1β (d), LIF (e), and OSM (f). Bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 5 mice/group). Statistical significance was measured by two-way ANOVA with Student-Newman–Keul’s Method of post hoc analysis. Statistical significance of at least p < 0.05 is denoted by * as compared to control and # as compared to METH-treated mice.