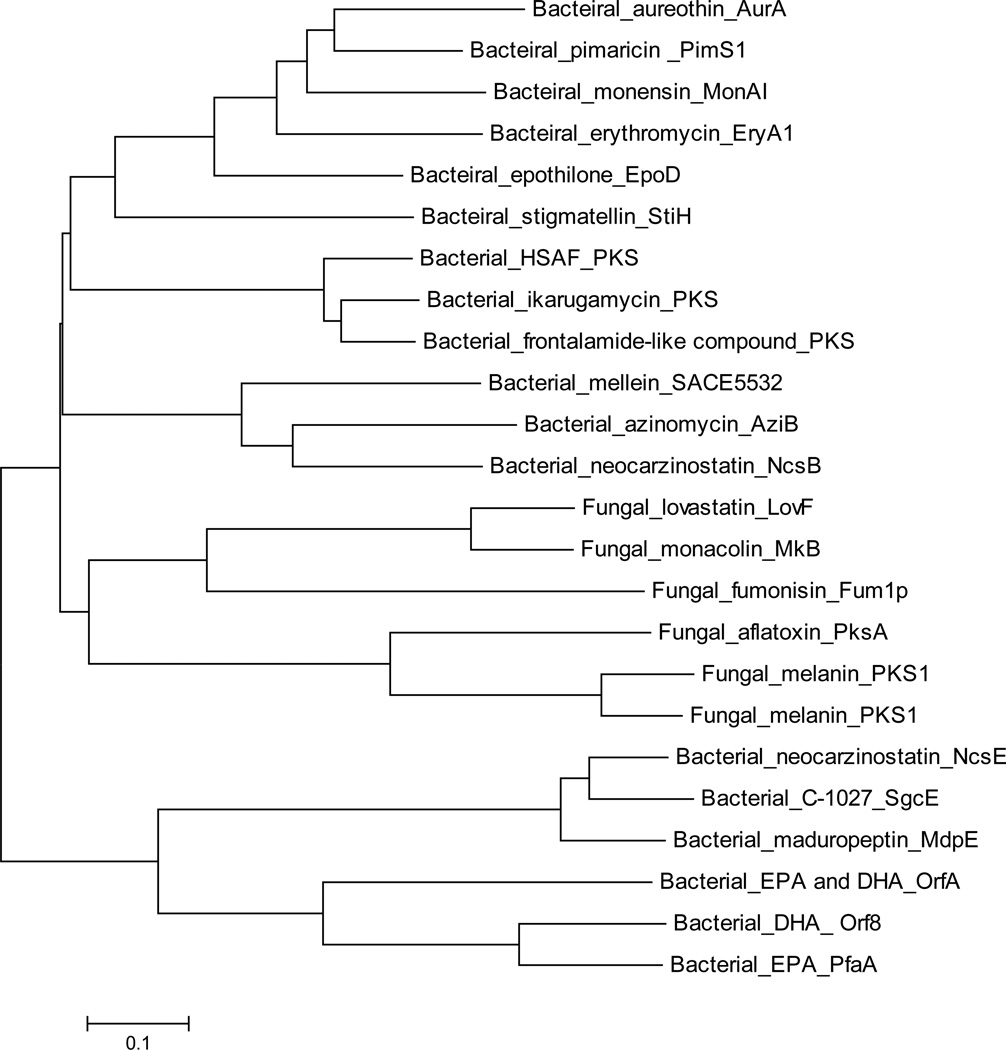
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic analysis of different types of PKSs based on the sequence of KS domains. Enzymes and their GenBank accession numbers are listed as follows: bacterial aromatic iPKS (3 sequences, including AziB for azinomycin biosynthesis, ABY83164.1; NcsB for neocarzinostatin biosynthesis, AAM77986.1; SACE5532 for mellein biosynthesis, YP_001107644.1); PTM type iPKSs (3 sequences, including PKS for HSAF biosynthesis, EF028635.2; PKS for ikarugamycin biosynthesis, KF954512.1; PKS for frontalamide-like compound biosynthesis from Streptomyces albus J1074, ABYC01000481); modular PKSs (6 sequences, including PimS1 module 1 for pimaricin biosynthesis, CAC20931.1; MonAI: module 1 for monensin biosynthesis, AAO65796.1; EryA1: module 2 for erythromycin biosynthesis, YP_001102988.1; AurA for aureothin biosynthesis, CAE02602.1; EpoD for epothilone AAF26921.1; StiH for stigmatellin CAD19092.1); HR-PKSs (3 sequences, including Fum1p for fumonisin biosynthesis, AAD43562.2; LovF for lovastatin biosynthesis, AAD34559.1; MkB for monacolin biosynthesis, ABA02240.1); NR-PKS (3 sequences, including PksA for aflatoxin biosynthesis from Aspergillus flavus, AAS90093.1; PKS1 for melanin biosynthesis from Colletotrichum lagenaria, BAA18956.1; PKS1 for melanin biosynthesis from Glarea lozoyensis, AAN59953.1); enediyne synthases (3 sequences, including SgcE for C-1027 biosynthesis, ZP_11383500.1; MdpE for maduropeptin biosynthesis, AAQ17110.2; NcsE for neocarzinostatin biosynthesis, AAM78012.1); PUFA synthases (3 sequences, including PfaA for EPA biosynthesis from Photobacterium profundum, AAL01060.1; Orf8 for DHA biosynthesis from Moritella marina, BAA89382.2; OrfA for EPA and DHA biosynthesis from Schizochytrium AAK72879.2). Similar sequences were aligned with ClustalW and the tree shown was generated using the MEGA 5.0).