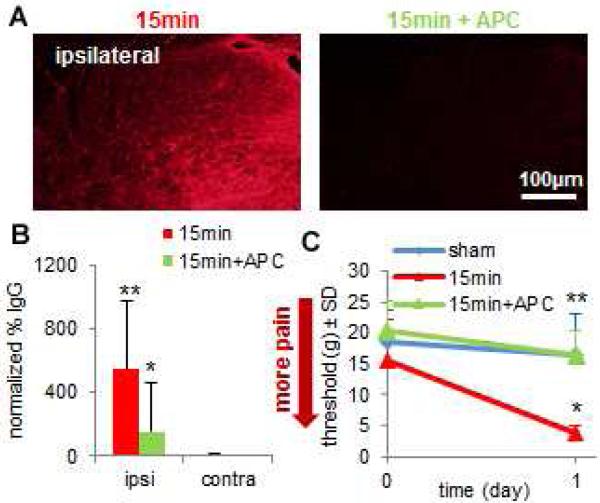
Fig. 3. Blocking BSCB breakdown with intravenous APC inhibits nociception after neural injury.
(A) Spinal IgG is reduced after APC treated 15-minute compression (15min+APC) compared to compression alone (15min). (B) A 15min compression significantly increases (**p=0.028) spinal IgG in the ipsilateral dorsal horn compared to the contralateral dorsal horn on day 1. Ipsilateral IgG for 15min+APC is significantly lower (*p<0.001) than 15min on day 1 and is not different from respective contralateral values. (C) Forepaw withdrawal threshold at day 1 is significantly reduced (*p=0.024) by a 15min compression compared to sham, whereas, 15min+APC exhibits a significantly higher (**p=0.012) withdrawal threshold than 15min, which is not different sham. All data represented as mean±SD.