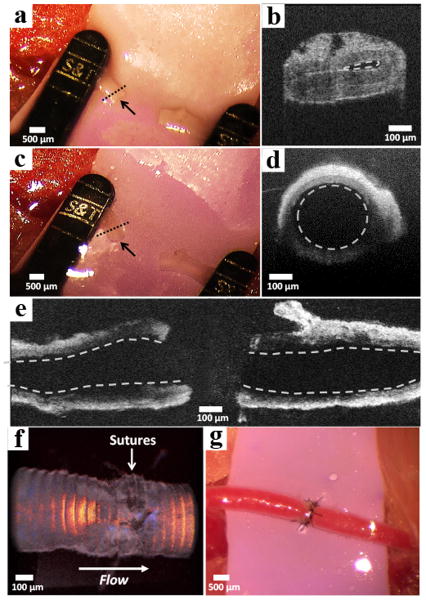
Figure 5. Assessment of vessel patency before and after gel-based anastomosis.
(a) Collapsed femoral artery of a mouse indicated by the black arrow. (b) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) of the severed vessel cross-section. Collapsed vessel lumen indicated by the dashed line. The image was collected at the region of the vessel indicated by the dashed line in panel a. (c) Distended end with open lumen of artery after injection of 2 wt% APC1 hydrogel indicated by the black arrow. (d) OCT of the vessel cross-section showing the distended lumen (dashed circle). The vessel was imaged at the region indicated by the dashed line in panel c. (e) Horizontal cross-section of the proximal (left) and distal (right) vessel walls showing open lumina (dashed lines) after hydrogel injection. (f) OCT volume Doppler depiction of anastomosed artery after irradiation where the red, orange, and yellow regions indicate uncompromised blood flow through the suture site. (g) Macroscopic appearance of anastomosed femoral artery with normal blood flow.