Figure 7.
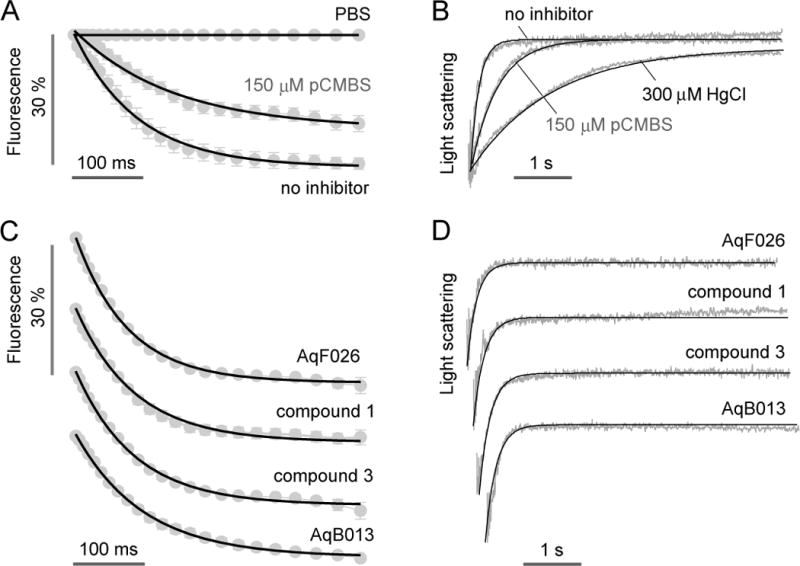
Water permeability and inhibitor testing in human erythrocytes. A. Microfluidics measurement of osmotic water permeability in untreated and 150 μM pCMBS-treated human erythrocytes. Flow rates were 400, 400, 200, 500, 500 μl/h, respectively, for the Na gluconate solution, erythrocyte suspension, PBS (center channel), mineral oil (top) and mineral oil (bottom). The Na gluconate gradient was 250 mM. B. Stopped-flow light scattering measurement of osmotic water permeability in human erythrocytes (250 mM Na gluconate gradient), with indicated inhibitors. C. Microfluidics measurement of osmotic water permeability in the presence of putative AQP1 modulators (at 50 μM). D. Stopped-flow light scattering measurement of osmotic water permeability for the same compounds (at 50 μM).
