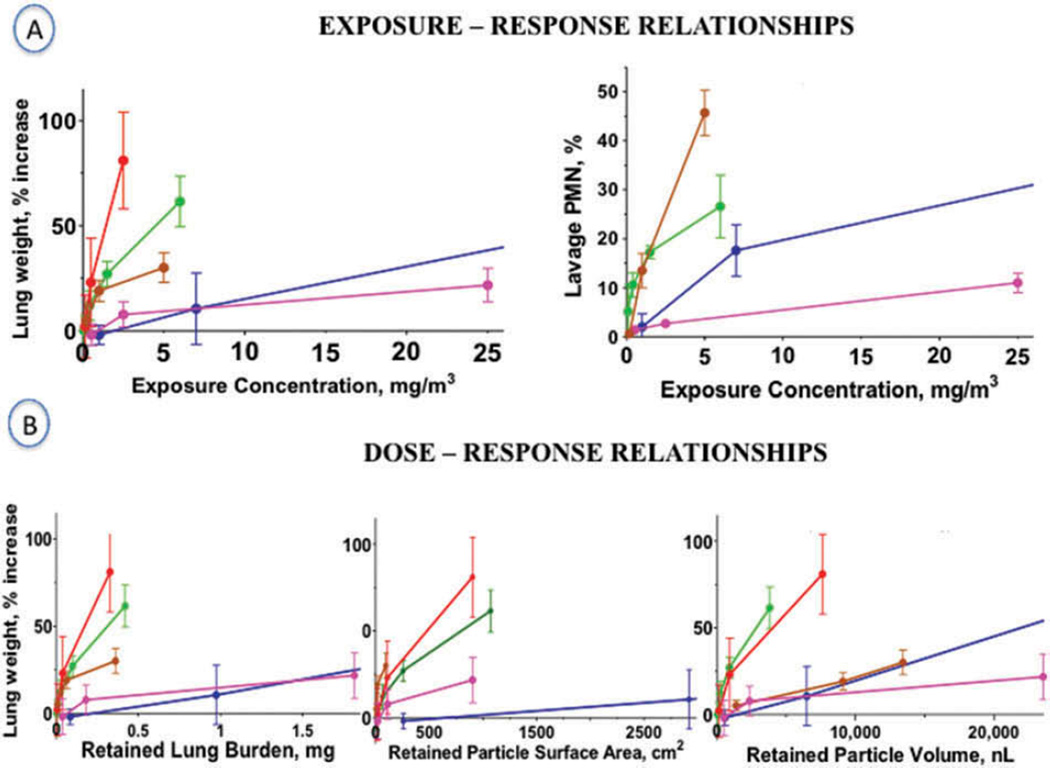
FIGURE 4. Exposure-Response and Dose-Response.
Exposure-Response and Dose-Response relationships of five 3-month inhalation studies in rats with MWCNT, CNF and CB. The carbon black (CB) study is added as a well studied low toxicity particle for comparison.
Percent increase in lung lavage neutrophils (PMN) and retained lung dose were not reported for all of the five subchronic rat inhalation studies. Thus, to approximate retained lung burden of the MWCNT study by Ma-Hock et al. and for the CNF study by DeLorme et al., deposited and retained doses were calculated with the MPPD model, Version 2.90.3, using MMAD and GSD data and the packing density of the materials provided by the authors and a normal rat-specific pulmonary retention halftime (T1/2) of 70 days as model inputs. This T1/2 is appropriate for the rats exposed to the lower concentrations; for the high concentrations and resulting high lung burdens, a prolongation of T1/2 has to be expected (for example, as determined by Pauluhn et al., 2010, Table 3). Therefore, the lung burdens calculated for the high dose groups of these two studies are likely underestimated. The x-axes have been truncated to better separate the individual MWCNT/CNF data, although as a consequence the high exposure/date points could not be displayed.
A: Lung weight and lung lavage neutrophil exposure-responses. B: Lung weight dose-responses based on retained lung burden expressed as mass, surface area and volume of the retained material.
 - MWCNT (Pauluhn, 2010);
- MWCNT (Pauluhn, 2010);  - MWCNT (Ma-Hock et al., 2009a);
- MWCNT (Ma-Hock et al., 2009a);  - CNF (DeLorme et al., 2012);
- CNF (DeLorme et al., 2012);  - CB (Elder et al., 2005);
- CB (Elder et al., 2005);  - MWCNT (Kasai et al., 2015).
- MWCNT (Kasai et al., 2015).