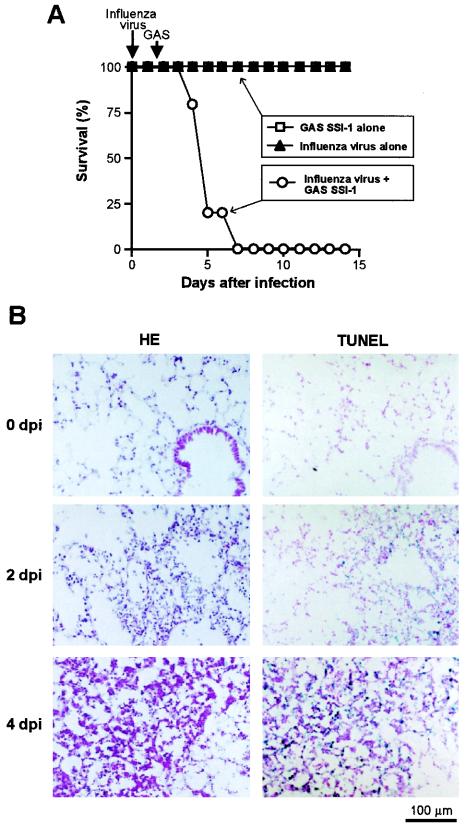
FIG. 6.
Pathological changes during severe GAS infections in mice. (A) Time profile of the survival rates of mice infected with either influenza virus alone or GAS strain SSI-1 alone and of mice infected with both influenza virus and GAS strain SSI-1. The model of severe GAS infection was produced in ddY mice, which received the influenza virus A/Aichi/2/68 (H3N2) strain by inhalation of 7 × 104 PFU/ml of viral suspension. Then, at 36 h after inhalation of the influenza virus, superinfection with GAS strain SSI-1, a clinical isolate from a TSLS patient, was produced by intranasal injection of 105 CFU of the bacteria in 20 μl of PBS. Severe diseases caused by fulminating GAS pneumonia and septicemia resulted. n = 5 for each group. P < 0.01 for groups infected with GAS SSI-1 and virus alone versus the GAS superinfection group by Fisher's exact probability test. (B) Pathological and apoptotic changes in mouse lungs occurring during severe GAS infection were studied histologically by HE staining and in situ by TUNEL assay of serial sections. 0 dpi (day postinfection), uninfected mice; 2 and 4 dpi, 2 and 4 days after GAS infection, respectively. See the text for details.