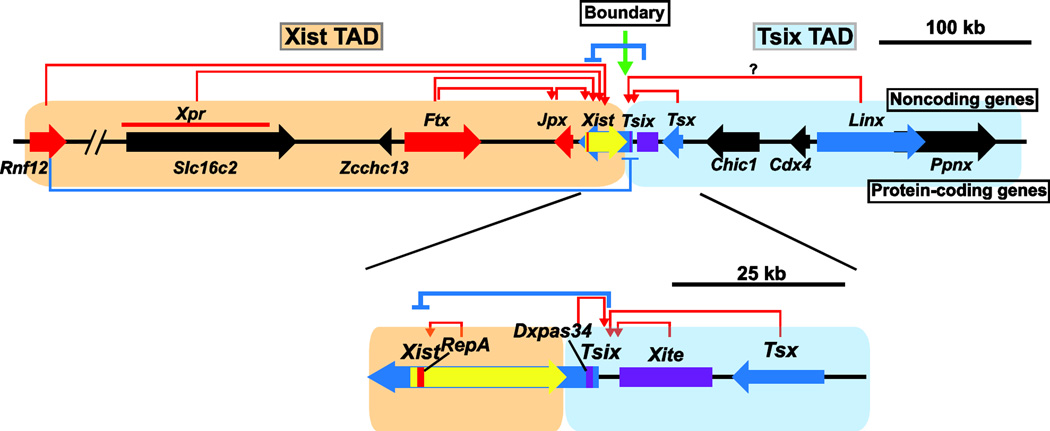
Fig. 1.
Functionally distinct topologically associating domains (TADs) at the Xic. The schematic of Xist and Tsix TADs, long noncoding genes, and a protein-coding gene at the Xic locus is shown; each of these plays a role in XCI. Yellow bold arrow indicates Xist. Red and Blue bold arrows indicate genes that activate and repress Xist, respectively. Black arrows indicate non-XCI-related genes to date. Purple boxes indicate enhancer-like region for Tsix. Names of long noncoding and protein-coding genes are shown above and below these bold arrows, respectively. Red and blue arrows indicate gene’s function as activator and repressor for Xist expression, respectively. The green arrow indicates the Xist/Tsix TAD boundary.