FIGURE 2.
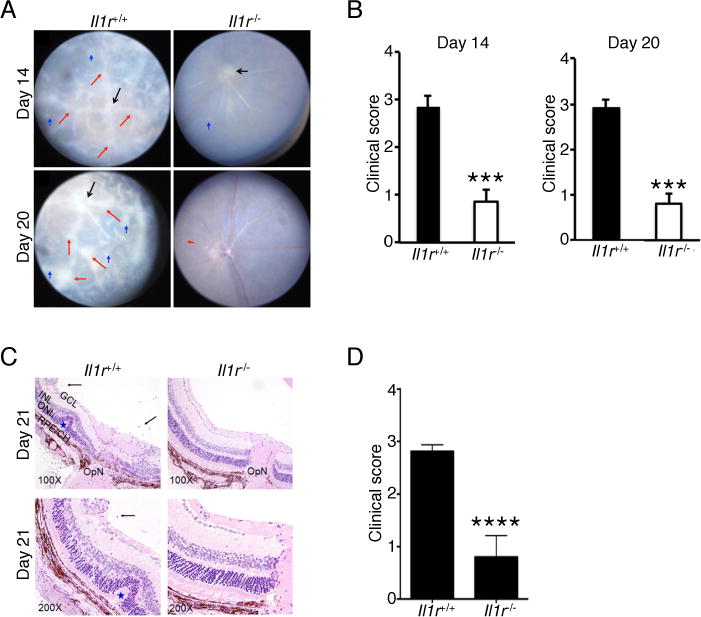
Il1r-deficient mice develop less severe EAU. EAU was induced in WT and Il1r−/− mice. (A) Fundus images of the eyes at days 14 and 20 after EAU induction. Compared to the Il1r−/− mice, the retinae of WT mice reveals obvious inflammation with blurred optic disc margins and enlarged juxtapapillary area (black arrows), retinal vasculitis with moderate or severe cuffing (red arrows), and yellow-whitish retinal and choroidal infiltrates (blue arrows). (B) Clinical score and assessment of disease severity were based on changes at the optic nerve disc or retinal vessels and retinal and choroidal infiltrates as described in the text. ***, P < 0.001. (C) Histological analysis of the retina at day 21 after EAU induction shows increased numbers of inflammatory cells in the vitreous (black arrows), retinal folds (blue asterisk) in retina of WT compared to Il1r−/− mice. (D) Significant reduction of histological score in Il1r−/− mice compared to WT mice. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments (total of 10 mice/group). ****, P < 0.0001. Sections were stained with H&E staining. V, vitreous, black arrow, infiltrated for inflammatory cells, Blue asterisk, retinal folds; OpN, optic nerve; GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL outer nuclear layer; RPE/CH retinal pigment epithelial cell layer; and choroid.
