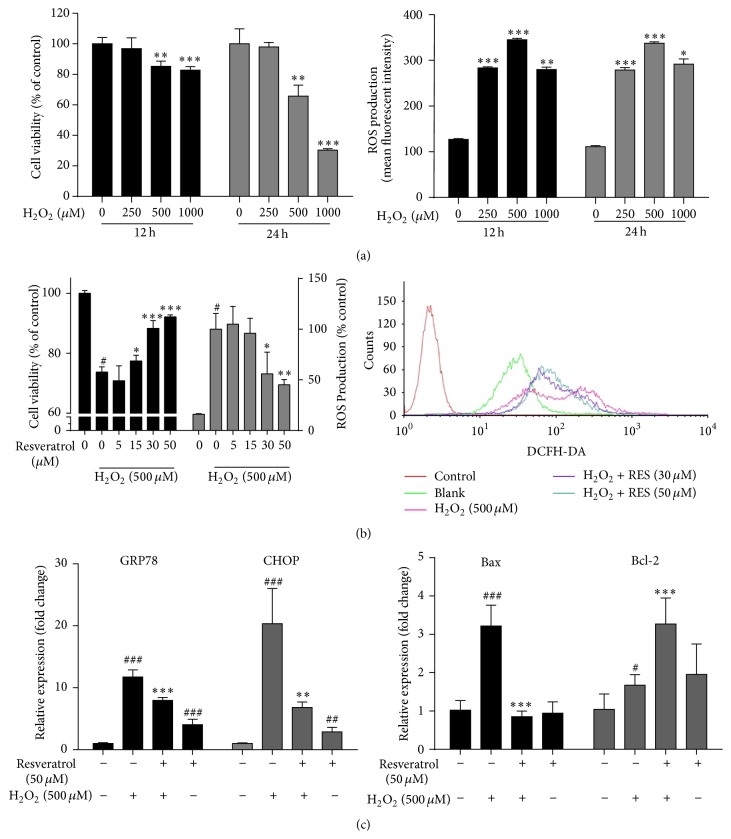
Figure 1.
Protective effects of resveratrol against H2O2-induced MAC-T cell death and ROS production. (a) MAC-T cells were treated with increasing concentrations of H2O2 (0, 250, 500, and 1000 µM) for 12 h or 24 h. Cell viability was measured by CCK-8 assay (left panel), and ROS concentration was measured by flow cytometer after being loaded with 10 µM DCFH-DA fluorescence probe for 30 min (right panel). ∗ p < 0.05, ∗∗ p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗ p < 0.001 significantly different from untreated cells. (b) MAC-T cells were pretreated with the indicated concentrations of resveratrol for 2 h, followed by H2O2 (500 μM) challenge for 24 h. Then the cell viability (black bars) and ROS concentration (grey bars) were determined (left panel). A representative flow cytometric histogram is shown (right panel). (c) MAC-T cells were pretreated with or without 50 μM of resveratrol for 2 h and then treated with or without 500 μM of H2O2. The mRNA expression of the endoplasmic reticulum stress markers GRP 78 and CHOP (4 hours after H2O2 treatment) and mitochondria-related cell apoptosis markers Bax and Bcl-2 (24 h after H2O2 treatment) was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR. Data are represented as mean ± SD from three independent experiments. # means significantly different from untreated cells. ∗ means significantly different from H2O2-treated cells.