Figure 4.
Phenotypic Characteristics of PPRD1-OE and pprd2+/− Plants and Their Crosses.
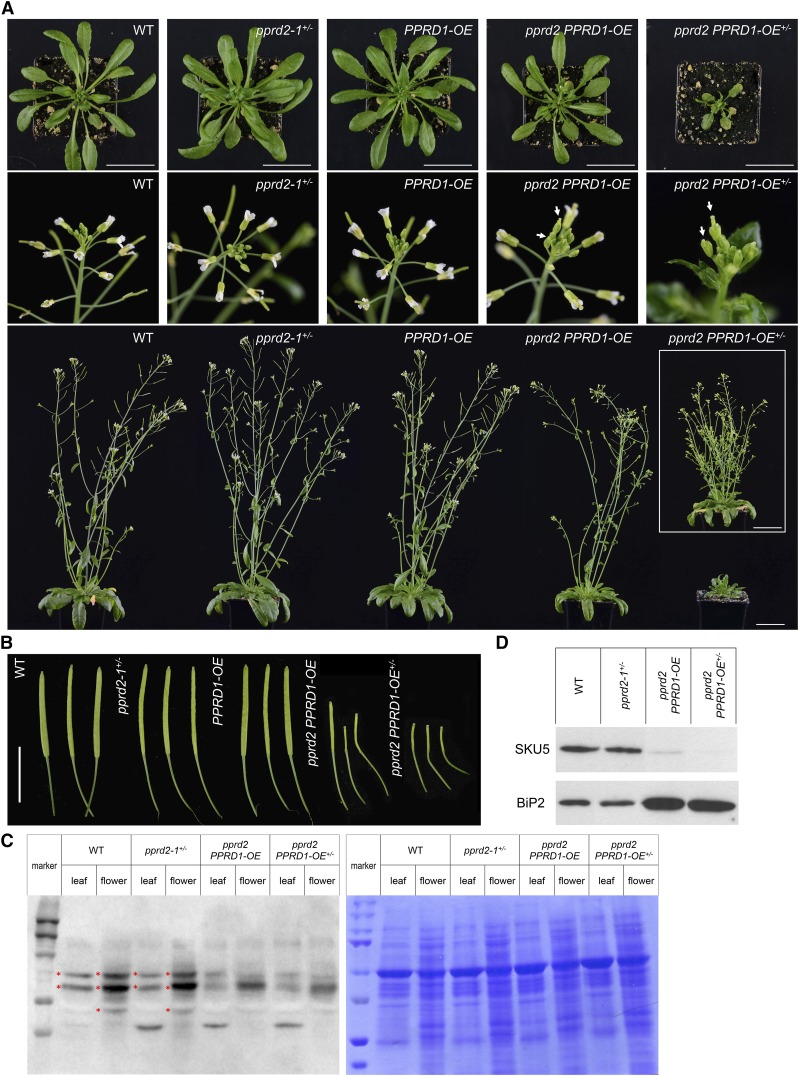
(A) Rosettes of 5-week-old plants (upper panel), flowers (middle panel), and whole 7-week-old plants (lower panel) are presented. Arrows indicate delayed flowering of pprd2 PPRD1-OE and pprd2 PPRD1-OE+/− lines. To illustrate that the pprd2 PPRD1-OE+/− plants show delayed rather than blocked development, the inset presents a 10-week-old plant. Bar = 5 cm.
(B) Siliques of 7-week-old (wild type, pprd2-1+/−, PPRD1-OE, and pprd2 PPRD1-OE) and 10-week-old (pprd2 PPRD1-OE+/−) plants. Bar = 1 cm.
(C) and (D) Analysis of glycosylated proteins in wild-type, pprd2-1+/−, pprd2 PPRD1-OE, and pprd2 PPRD1-OE+/− plants. Protein extracts from leaves and flowers were separated by SDS-PAGE and blots were probed with Concanavalin A labeled with horseradish peroxidase (left image) (C). Gel stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue is presented in right image. Marker lines contain PageRuler Prestained Protein Marker. Asterisks mark bands present in wild-type extracts but absent in pprd2 lines. Alternatively, blots were probed with anti-SKU5 or anti-BiP2 antibody (D). In pprd2 homozygotes, SKU5 protein is (nearly) absent, while the BiP2 level is elevated compared with the wild type. Equal amounts of protein were loaded in all lanes.
See also Supplemental Figures 6 and 7 and Supplemental Table 3.