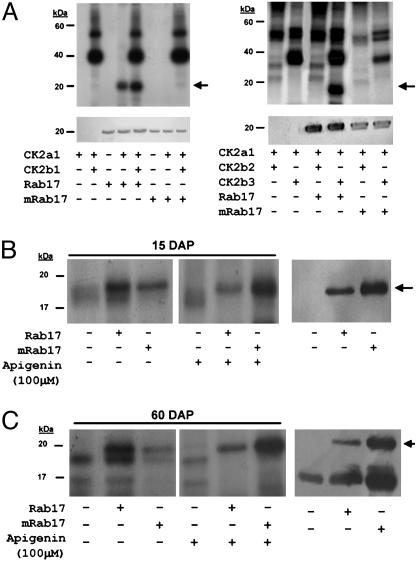
Fig. 4.
Phosphorylation of Rab17 by protein kinase CK2. (A) In vitro phosphorylation of Rab17 by CK2. (Upper) Autoradiography of the different in vitro CK2 assays. (Lower) Western blot of the above samples using anti-Rab17 antibody, confirming the position and amounts of recombinant Rab17 or mRab17 added to the in vitro CK2 phosphorylation reaction. The combinations of different CK2α/β subunits, addition of recombinant Rab17 or mRab17 as substrate, and presence or absence of phosphorylation are indicated underneath each lane. (B and C Left) Autoradiography of in vitro CK2 assays with young embryo extracts 15 days after pollination (B) or dry embryo extracts 60 days after pollination (C), plus recombinant Rab17 or mRab17 as substrate, with or without the CK2 inhibitor apigenin. (Right) Western blot of the first three lanes on the left using the antiRab17 antibody indicating the presence of the endogenous Rab17 present in the mature maize extracts and in those samples where exogenous recombinant Rab17 and mRab17 proteins have been added. Addition of recombinant Rab17, mRab17, or apigenin is indicated underneath for each lane.