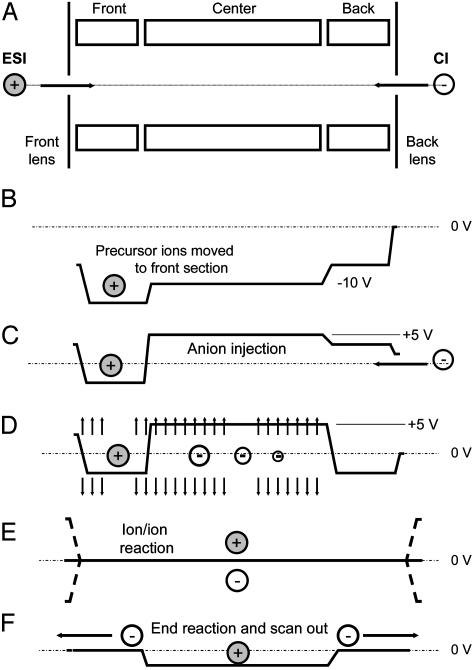
Fig. 4.
Schematic of steps involved in the operation of the LTQ mass spectrometer for peptide sequence analysis by ETD. (A) Injection of multiply protonated peptide molecules (precursor ions) generated by ESI. (B) Application of a dc offset to move the precursor ions to the front section of the linear trap. (C) Injection of negatively charged reagent ions from the CI source into the center section of the linear trap. (D) Application of a supplementary dipolar broadband ac field to eject all ions except those within 3 mass-unit windows centered around the positively charged precursor ions and the negatively charged electron-donor reagent ions. (E) Removal of the dc potential well and application of a secondary RF voltage (100 V zero to peak, 600 kHz) to the end lens plates of the linear trap to allow positive and negative ion populations to mix and react. (F) Termination of ion/ion reactions by axial ejection of negatively charged reagent ions while retaining positive ions in the center section of the trap. This is followed by mass-selective, radial ejection of positively charged fragment ions to record the resulting MS/MS spectrum.