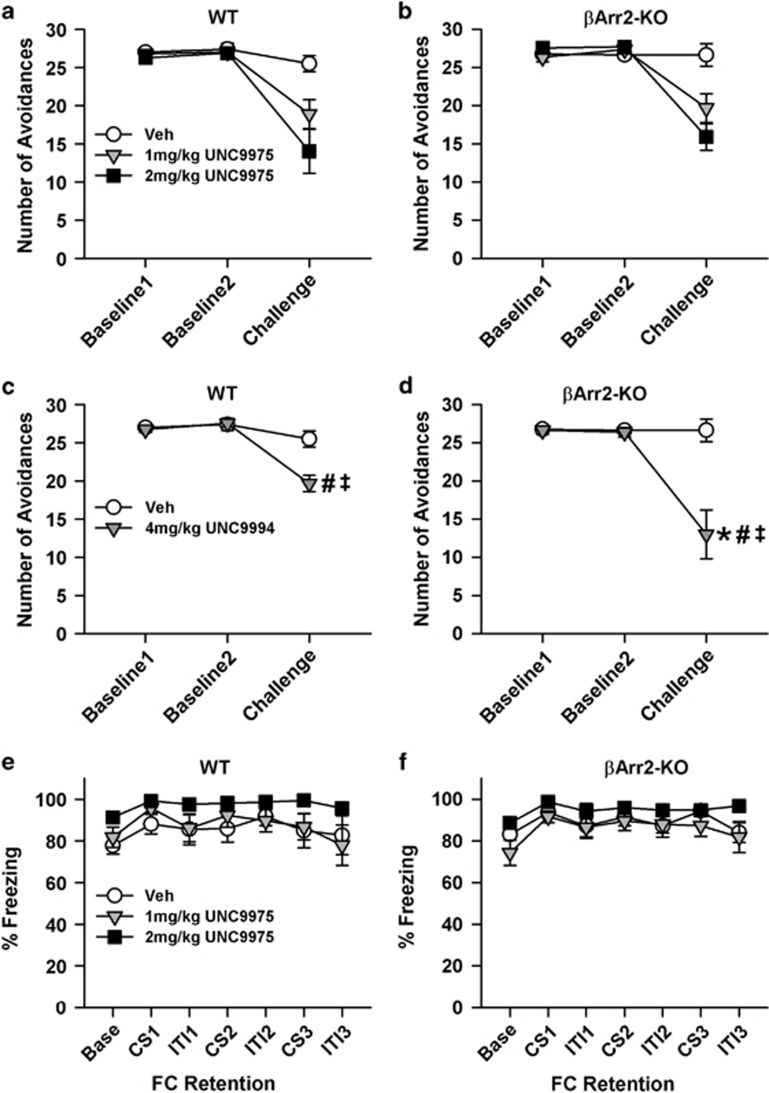
Figure 4.
UNC9975 and UNC9994 reduce CAR in βArr2 mice but do not affect associative fear conditioning. Once CAR responses were stable, mice were treated the next day with vehicle (Veh) or a UNC compound, and assessed 30 min later. (a, b) Effects of UNC9975 on CAR responses by WT and βArr2-KO mice. RMANOVA for CAR with UNC9975 revealed a significant within-subjects day effect (F(2, 90)=71.42, p<0.001) and a significant day-by-treatment interaction (F(4, 90)=15.70, p<0.001). In addition, the between-subjects effect of treatment was significant (F(2, 45)=12.56, p<0.001). (c, d) Effects of UNC9994 on CAR responses by WT and βArr2-KO mice. RMANOVA for CAR with UNC9994 demonstrated a significant within-subjects day effect (F(2, 62)=36.34, p<0.001) and significant day-by-treatment (F(2, 62)=26.00, p<0.001) and day-by-treatment-by-genotype interactions (F(2, 62)=4.10, p=0.021). The between-subjects treatment effect was significant (F(1, 31)=22.22, p<0.001); the effects of genotype (F(1, 31)=3.38, p=0.076) and the treatment-by-genotype interaction (F(1, 31)=3.60, p=0.067) were marginally significant. (e, f) Effects of UNC9975 on fear conditioning in WT and βArr2-KO mice. RMANOVA at retention testing revealed significant within-subjects effects of time (F(6, 324)=9.89, p<0.001). Base, baseline; CS, conditioned stimulus; ITI, intertrial interval; FC, fear conditioning. N=8–11 mice/genotype/treatment condition. The data are presented as mean±SEM; *p<0.05, WT vs βArr2-KO; #p<0.05, within genotype vs Veh; ‡p<0.05, within genotype vs baseline responses.