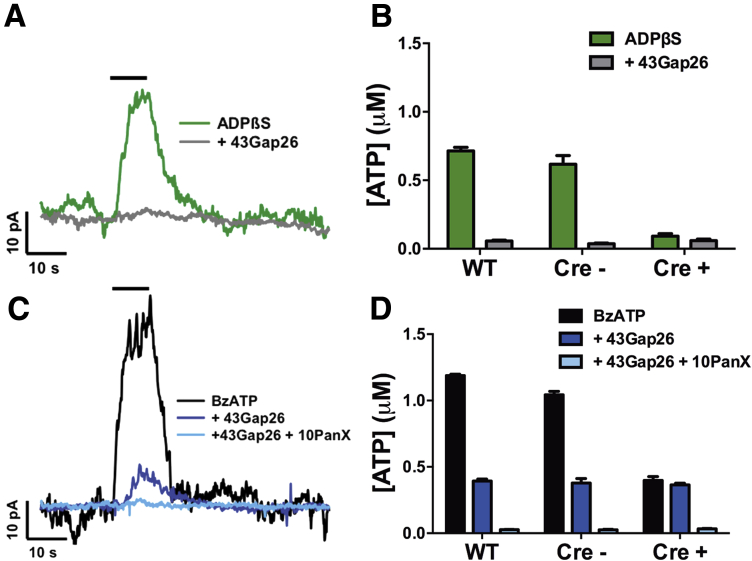
Figure 3.
Stimulation of enteric glial P2Y1 receptors (P2Y1Rs) elicits connexin-43 (Cx43)-dependent adenosine triphosphate (ATP) release. (A, C) Representative traces and (B, D) quantified measurements of ATP release from the mouse myenteric plexus obtained with ATP-selective electrodes. Glial P2Y1Rs were directly stimulated with the P2Y1R agonist, adenosine 5′-[β-thio]diphosphate trilithium salt (ADPβS, A, B: 100 μM), or by eliciting neuron-to-glia communication with the neuronal P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) agonist 2′(3′)-O-(4-benzoylbenzoyl)adenosine 5′-triphosphate triethylammonium salt (BzATP, C, D: 300 μM), in the presence or absence of the Cx43 mimetic peptide 43Gap26 (100 μM), the pannexin-1 mimetic peptide 10Panx (100 μM), or in tissue from Cx43i-cKO mice after the selective ablation of glial Cx43 (Cre+ knockout or Cre− littermate controls). n = 3 animals.