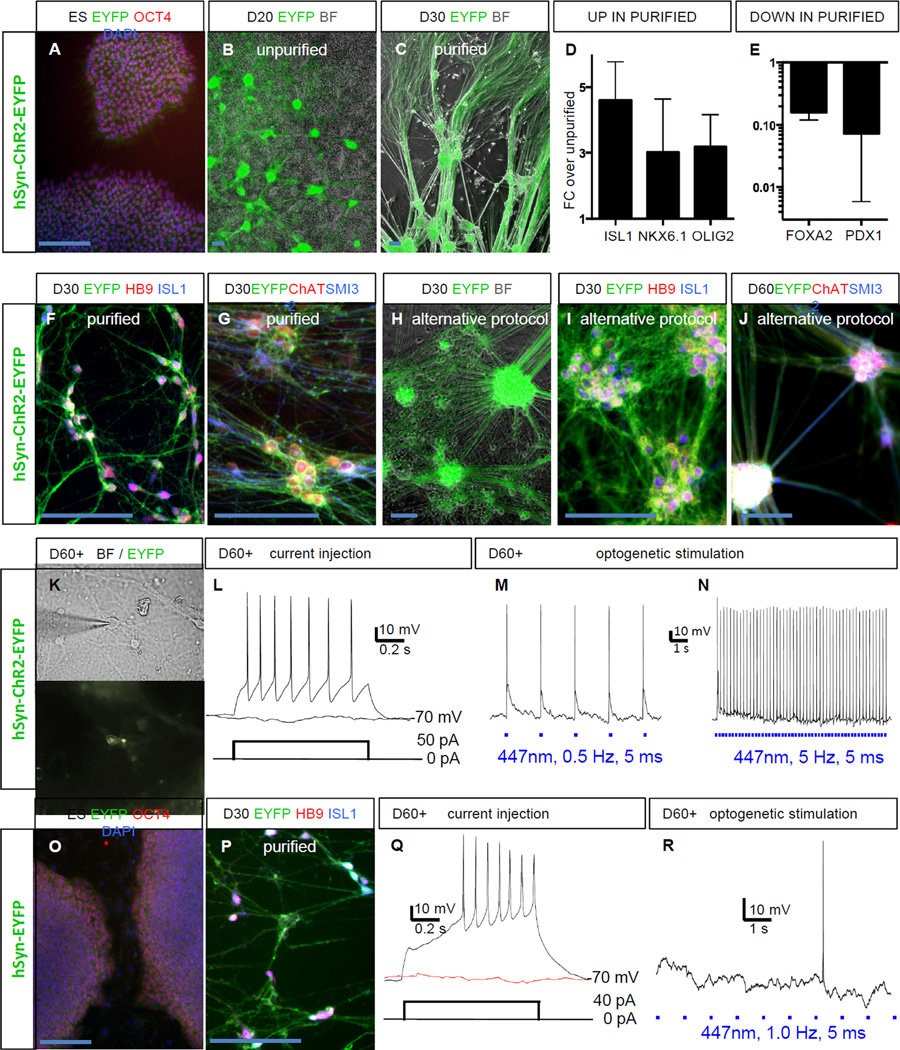
Figure 1. Optogenetic control in hPSC derived spinal motorneurons (MNs).
(A) Clonal hESC line carrying the hSyn-ChR2-EYFP transgene staining for OCT4 (POU5F1) and DAPI.
(B) At day 20 (D20) MN clusters express ChR2-EYFP, bright field (BF).
(C) After purification MN clusters are enriched.
(D) qRT-PCR, after purification sMN markers are up-regulated.
(E) qRT-PCR, after purification non-neuronal markers are down-regulated.
(F) At day 30 spinal MNs express ChR2-EYFP and stain for HB9 and ISL1.
(G) At day 30 spinal MNs co-stain for ChAT and SMI32.
(H) Alternative protocol ChR2-EYFP+ MNs.
(I) At day 30 spinal MNs (alternative protocol) express ChR2-EYFP, HB9 and ISL1.
(J) At day 60 spinal MNs (alternative protocol) express ChR2-EYFP, ChAT and SMI32.
(K) Neuron in bright field and EYFP channel chosen for electrophysiology.
(L) Beyond day 60 (D60+) hESC-derived MNs fire action potentials in response to depolarizing current injection.
(M, N) Mature ChR2+ hESC-derived MNs faithfully fire action potentials in response to optogenetic stimulation.
(O) Clonal hESC line carrying the hSyn-EYFP transgene staining for OCT4 and DAPI.
(P) At day 30 purified spinal hESC-derived MNs express EYFP, HB9 and ISL1.
(Q) Mature EYFP+ hESC-derived MN fires action potentials in response to current injection.
(R) Mature EYFP+ hESC-derived MNs do not respond to light stimulation.
Scale bars 100 µM. Error bars represent SEM.