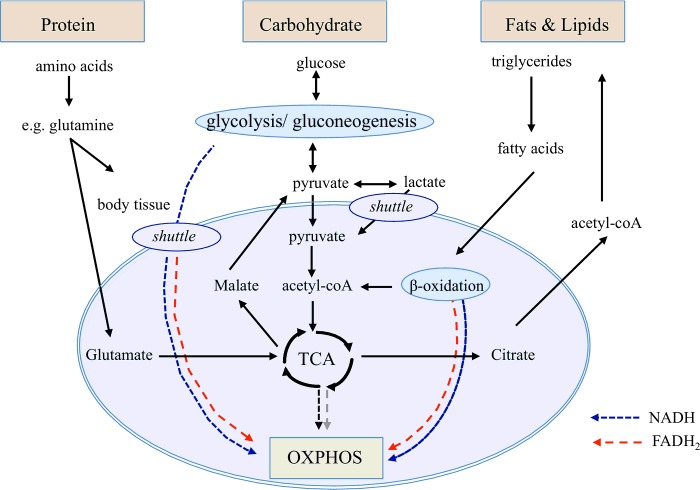
Figure 4. Nutrient metabolism.
Proteins: The first step in protein metabolism is to break it into its constituent amino acids. The second step is to break down amino acids into their constituent parts. One important amino acid is glutamine. Mitochondrial utilization of glutamine begins with a two-step conversion of glutamine to 2-oxogluterate, typically by glutaminase and glutamate dehydrogenase. 2-Oxogluterate can be either oxidized to succinate (standard TCA cycle) or reductively carboxylated (reverse TCA cycle) to isocitrate and then to citrate. Glutamine-derived malate can then be transported to the cytoplasm through the process of glutaminolysis to generate pyruvate and lactate. This reverse TCA cycle generates glutamine-derived citrate that can then be transported to the cytoplasm to generate acetyl CoA for anabolic processes such as fatty acid synthesis. Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are made out of simple sugars such as glucose. The first step of carbohydrate metabolism is glycolysis. It is the metabolic process that converts glucose into two molecules of pyruvate. The second step of carbohydrate metabolism occurs in the mitochondria. Here pyruvate is oxidized to acetyl-CoA and CO2 by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells and in the cytosol of prokaryotes. In a third step, when oxygen is present, the mitochondria will undergo aerobic respiration, which leads to the TCA cycle. Fat: Once the fatty acids have been transported to the mitochondrial matrix via the carnative pathway β-oxidation of fatty acyl-CoA occurs in a four step process. Assuming an even numbered carbon chain fully saturated fatty acid each cycle of β-oxidation produces one FADH2, one NADH and one acetyl-CoA (which produces one FADH2 and three NADH through the TCA cycle). This gives a total of two FADH2 and four NADHs inputs per cycle of β-oxidation or a FADH2/NADH ratio of approximately 0.5. But the very last pair of carbon atoms in a saturated fat already comprises acetate attached to CoA, so they can simply enter the TCA as acetyl-CoA (producing one FADH2 and three NADH).