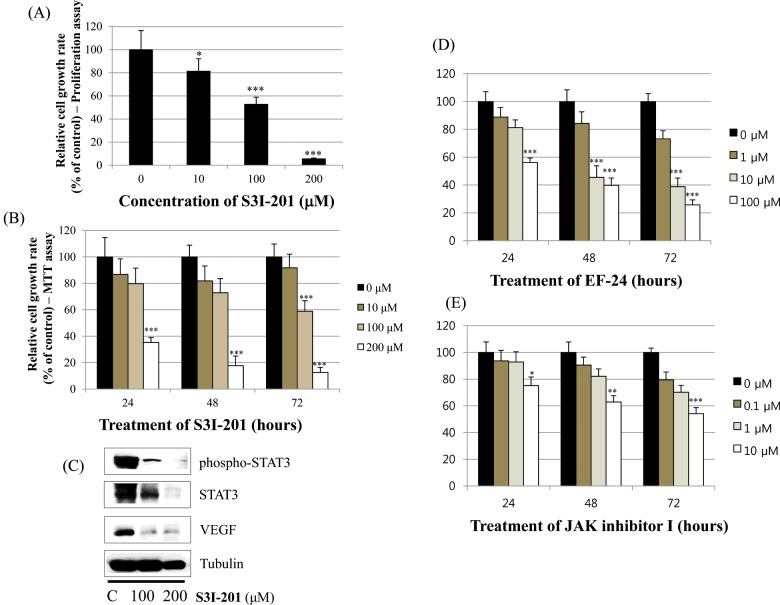
Figure 8. Effect of the STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 on the growth of BT-474 cells.
(A) BT-474 cells were treated with different doses of the STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 (0–200 μM). After 72 h, the cell viability was assessed using a cell proliferation assay. (B) BT-474 cells were treated with different doses of the STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 (0–200 μM). The relative cell growth rate was measured by MTT assay after 24 h, 48 h and 72 h. The growth rate of the vehicle-treated cells was set to 100%, and the relative decrease in cell viability resulting from the S3I-201 treatment was expressed as a percentage of the control. Data are shown as the means of three independent experiments (error bars denote S.D.). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. (C) BT-474 cells were treated with the STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 for 24 h. Whole-cell lysates were analysed by western blotting with anti-p-STAT3, anti-STAT3, anti-VEGF and anti-tubulin antibodies. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments that gave similar results. (D) (E) BT-474 cells were treated with different doses of the HIF-1α inhibitor EF-24 (0–100 μM) or JAK inhibitor I (0–10 μM). The relative cell growth rate was measured by MTT assay after 24 h, 48 h and 72 h. The growth rate of the vehicle-treated cells was set to 100%, and the relative decrease in cell viability resulting from the treatment was expressed as a percentage of the control. Data are shown as the means of three independent experiments (error bars denote S.D.). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.