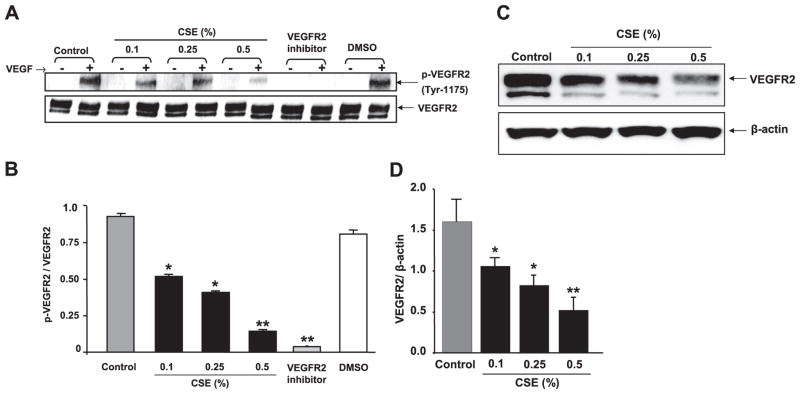
Figure 5.
CSE concentration dependently decreased VEGFR-2 and VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 (tyr 1175) in HMVEC-Ls. A) CSE- or VEGFR-2 inhibitor-treated cells (2 h) were incubated with VEGF as mentioned in Materials and Methods. Phosphorylated and total VEGFR-2 levels were measured using immunoblotting with rabbit monoclonal anti-p-VEGFR (tyr-1175, Cell Signaling Technology) and rabbit monoclonal anti-VEGFR-2 antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology), respectively. The VEGFR-2 blot showed two bands: 230 kDa, fully glycosylated functional receptor; and 200 kDa, semiglycosylated nonfunctional receptor. Phosphorylation was seen only in fully glycosylated functional receptor. CSE down-regulated VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner. Pretreatment of cells with VEGFR-2 inhibitor (NVP-AAD777, 1 μM) abolished the VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 phosphorylation. B) Histograms represent mean ± SE relative VEGFR-2 phosphorylation (n=3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control groups. C) VEGFR-2 levels were measured after cells were treated with CSE (0.1–0.5%) for 12 h using immunoblotting. VEGFR-2 blot showed two bands: 230 kDa, fully glycosylated functional receptor; and 200 kDa, semiglycosylated nonfunctional receptor. VEGFR-2 levels (230 kDa band) were significantly decreased in response to CSE in a concentration-dependent manner. D) Histograms represent mean ± SE relative expression levels of VEGFR-2 (n=3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. control groups.