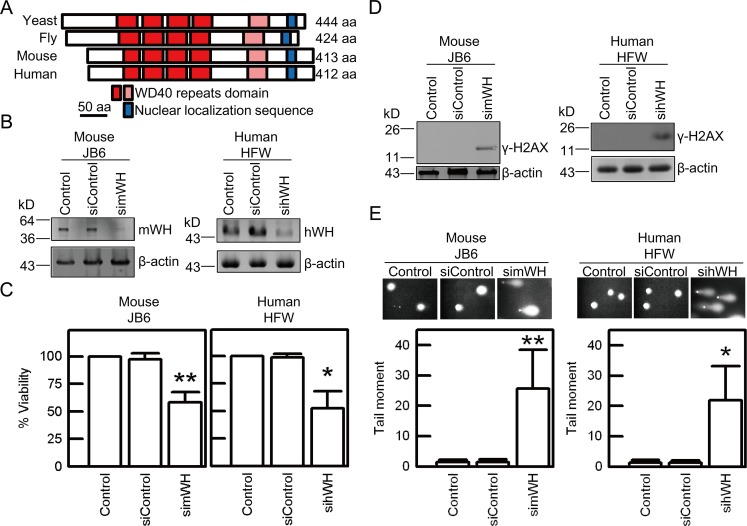
Fig 1. Depletion of Wuho protein (WH) induces loss of viability and DNA damage in mouse JB6 and human HFW cell lines.
Wuho (WH) homologues display similarity in protein sequence and function of cellular protection. (A) Sequence conservation of Wuho shown by alignment of WH homologues in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae), fly (Drosophila melanogaster), mouse (Mus musculus), and human (Homo sapiens), based on a previous study [21]. Dark and light red boxes represent WD40 repeats of high and low similarity, respectively, and blue boxes represent nuclear localization sequence. Scale bar is 50 amino acids. (B) Mouse Wuho protein (mWH) and human Wuho protein (hWH) were depleted by treatment of 25 nM of mWH siRNA (simWH) or hWH siRNA (sihWH) in cultured cells for 72 h. No changes in WH levels were observed in Control (cells without treatment) or siControl (cells treated with control siRNA) groups. (C) Depletion of WH causes loss of viability as determined by MTT assays. (D) Depletion of WH induces DNA damage revealed by γ-H2AX staining. (E) DNA damage monitored by neutral comet assay. The levels of DNA double strand breaks were quantified as tail moment (the product of tail intensity and tail length) shown at lower panels. Single asterisk and double asterisks indicate significant differences when compared with the control groups at p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 levels, respectively, according to Student’s t test.