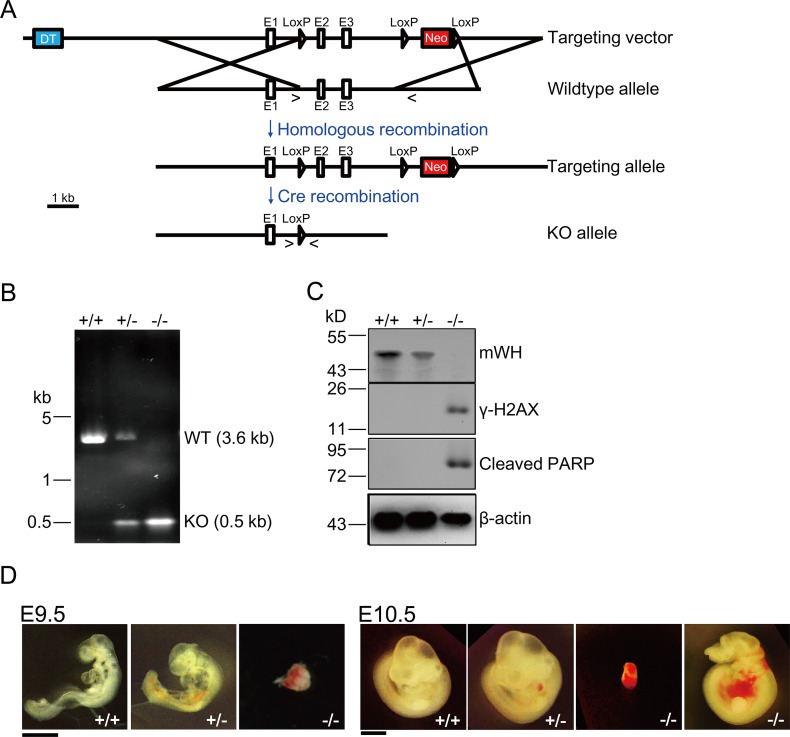
Fig 5. Mouse Wuho (mWh) is an essential gene.
(A) Gene targeting strategy. The gene targeting vector is a construct harboring positive (neomycin resistant gene [Neo], red) and negative (diphtheria toxin gene [DT], blue) selection markers. Through homologous recombination, the genomic region with exons 2 (E2) and 3 (E3) of mWh was replaced and resulted in the introduction of one loxP site before E2, and the Neo cassette flanked by two loxP sites in Intron 3. Subsequently, E2 and E3 were deleted by Cre recombinase through recombination between two distal loxP’s. The symbols “>” and “<” represent the locations of forward and reverse primers used in PCR for genotyping. The PCR products are 3.6 kb from in wild type allele and 0.5 kb from knockout allele. (B) A representative genotyping experiment for embryos of E9.5 from heterozygous parents. PCR products can distinguish among genotypes of +/+, +/-, and -/-. (C) Knockout of mWh results in DNA damage and apoptosis. The embryos genotyped in (B) were processed for western blot to examine expression of mWH, appearance of γ-H2AX for DNA damage, Cleaved PARP for apoptosis, and actin as loading controls. (D) Development of -/- embryos at E9.5 (left panel) and 10.5 (right panel) is abnormal. In E10.5 -/- embryos, they show varying morphology, potentially due to different degrees of resorption. Severe extents of resorption and are small (the left one of -/-). The other null embryo (the right one of -/-) show minor morphological defects and has brain development defects and internal bleeding. Scale bar is 1 mm.