Fig 1. Reaction sequence for the biosynthesis of hydroxylated alkylpyrones as sporopollenin building blocks.
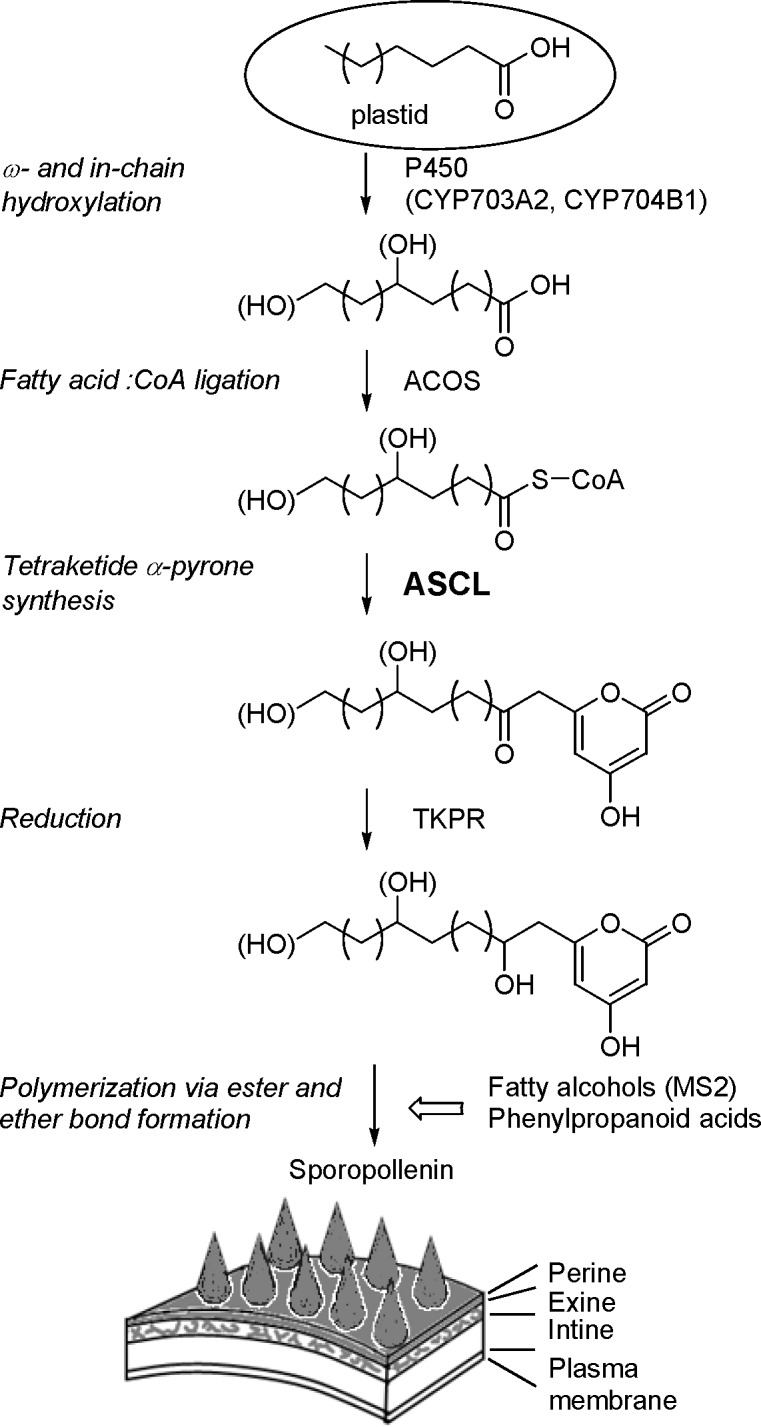
Medium- to long-chain fatty acids are produced in plastids and then translocated out to be used for the consecutive action of enzymes in sporopollenin biosynthesis. This proposed pathway produces sporopollenin building blocks that are polymerized along with fatty alcohols and phenylpropanoid acids on the surface of the spore or pollen wall by the formation of ester and ether linkages. Enzymes are listed to the right of the arrows with their corresponding reactions on the left. ACOS, acyl-CoA synthetase; ASCL, anther-specific chalcone synthase-like enzyme; MS2, Male Sterility 2; TKPR, tetraketide α-pyrone reductase.
