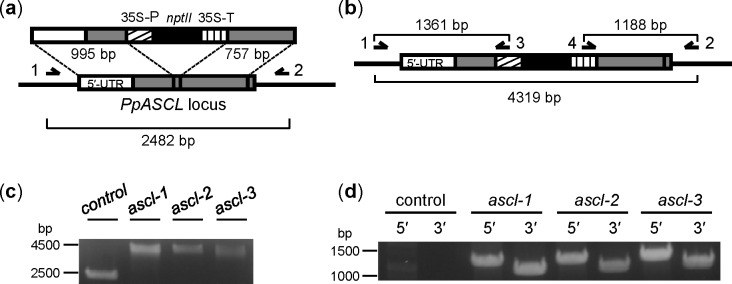
Fig 2. Strategy for targeted knockout of PpASCL and genotyping of the resulting stable transformants by PCR.
(a) Schematic diagram of insertion of the linear knockout construct into the PpASCL locus via double homologous recombination. 35S-P, CaMV 35S promoter; nptII, neomycin phosphotransferase II gene; 35S-T, CaMV 35S transcription termination signal. (b) Schematic diagram of recombined gene locus after successful insertion. Expected PCR product sizes based on sequence information are shown. Single-headed arrows denote the locations of primers specific to PpASCL (Primers 1 and 2, which bind to genomic DNA sequences located outside the locus-specific regions used for homologous recombination) or to the nptII resistance cassette (Primers 3 and 4) used in the PCR analyses. Primer 1, ASCL-gDNA-F; 2, ASCL-gDNA-R; 3, pTN182-5ʹ-R; 4, pTN182-3ʹ-F. Primer sequences are provided in S1 Table. (c) PCR products using locus-specific primers 1 and 2 with DNA from untransformed control and each of three stable putative PpASCL knockout lines: ascl-1, -2 and -3. (d) PCR products, indicative of 5′ and 3′ recombination between the knockout vector and homologous DNA in the PpASCL locus, using primers 1 plus 3 (5ʹ recombination) and primers 2 plus 4 (3ʹ recombination). Amplified DNA products were resolved electrophoretically on 1.2% agarose gels and visualized by ethidium bromide fluorescence.