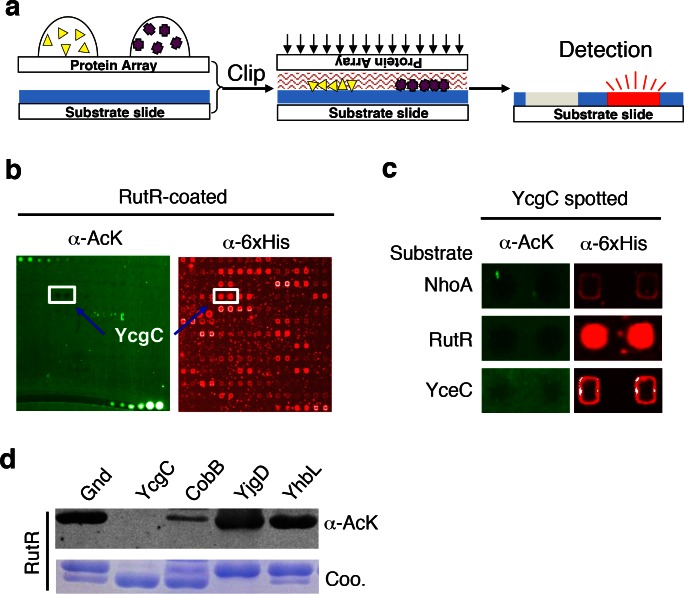
Figure 1. Screening the Escherichia coli proteome to discover new KDACs using the ‘clip-chip’ strategy.
(a) Schematic of the ‘clip-chip’ strategy. (b,c) Identification of YcgC as a potential protein deacetylase. E. coli proteome chips were clipped onto three substrate slides separately coated with acetylated RutR, NhoA, and YceC. After incubation in a protein deacetylase buffer, the reactions were terminated by adding wash buffers, followed by a signal detection step with a pan α-AcK antibody coupled with a Cy3-labeled secondary antibody as detection reagent to visualize the loss of signals (e.g., black holes in (b,c). To determine the identity of proteins that generated the holes, the substrate slide was subsequently probed with an α-6xHis antibody followed by a Cy5-conjugated secondary antibody. (d) Using acetylated RutR proteins purified from E. coli, of the four candidates tested, YcgC showed robust deacetylation activity in vitro. Equal amounts of RutR proteins were used in each reaction and loss of acetylation was detected with the pan α-AcK antibody.