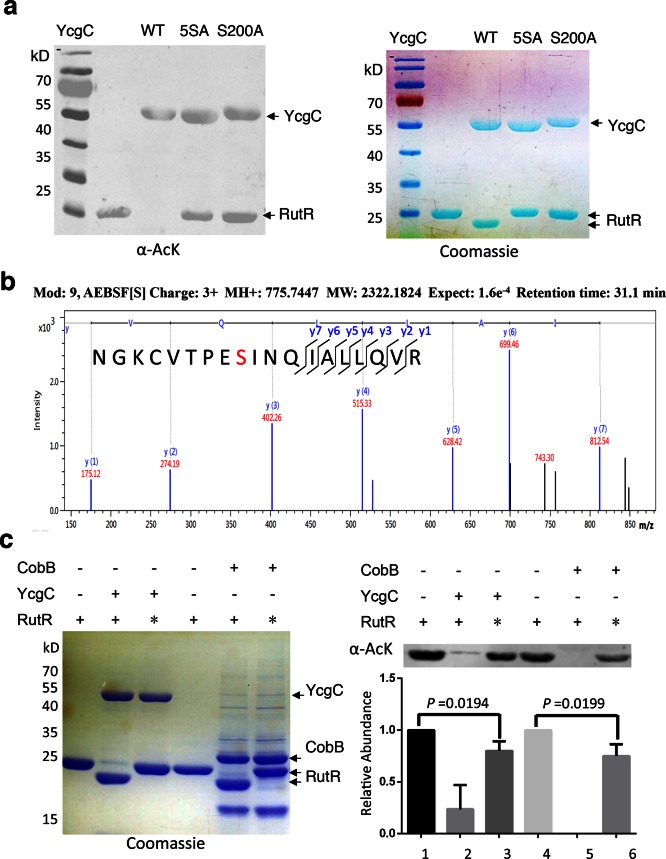
Figure 3. S200 is critical for YcgC’s deacetylation activity.
(a) Two mutants of YcgC, that is, S S8/10/73/77/200A and S200A were constructed through gene synthesis. In vitro assays of the KDAC activity of these two mutants on RutR demonstrated that their KDAC activities were completely abolished. (b) S200 on YcgC was identified as an AEBSF binding site by LC-MS/MS analysis. YcgC was incubated with AEBSF, then trypsin digested and subjected to MS/MS analysis. Upon AEBSF-mediated sulfonation, a 183 Da molecular weight increase is predicted. (c) In vitro assays of the KDAC activity of YcgC on heat-denatured RutR demonstrated that YcgC was still active (right panel), while the downshift band disappeared (left panel). Similar results were observed when heat-denatured RutR was treated with CobB. KDAC: Lysine deacetylase; LC-MS/MS: Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry; AEBSF: 4-(2-Aminoethyl)benzenesulfonyl fluoride; WT: Wild type.
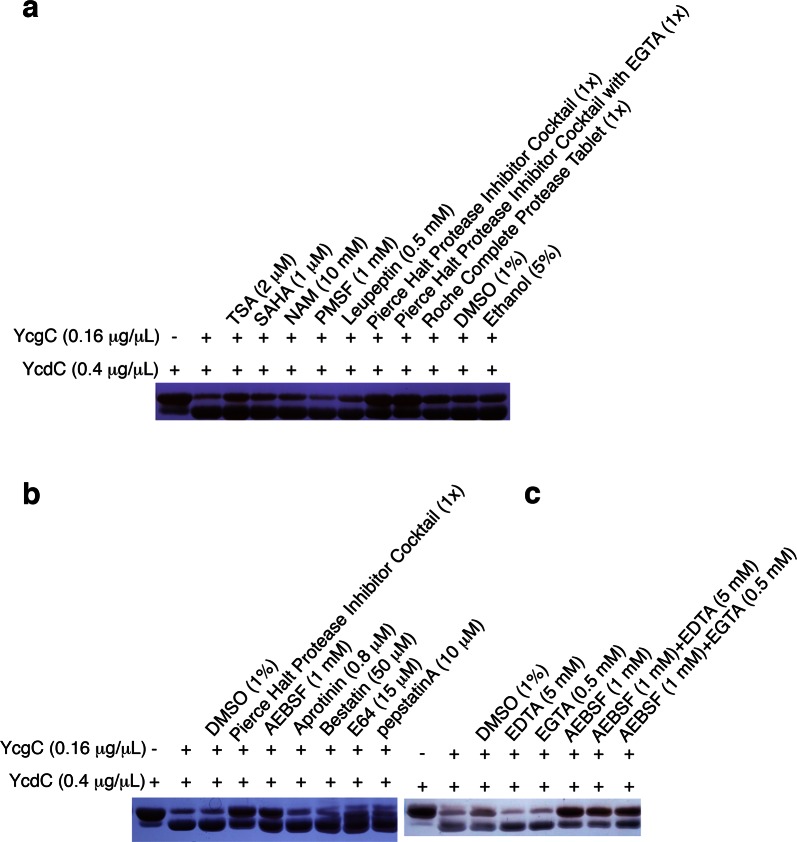
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. YcgC’s protein deacetylase activity is inhibited by AEBSF.
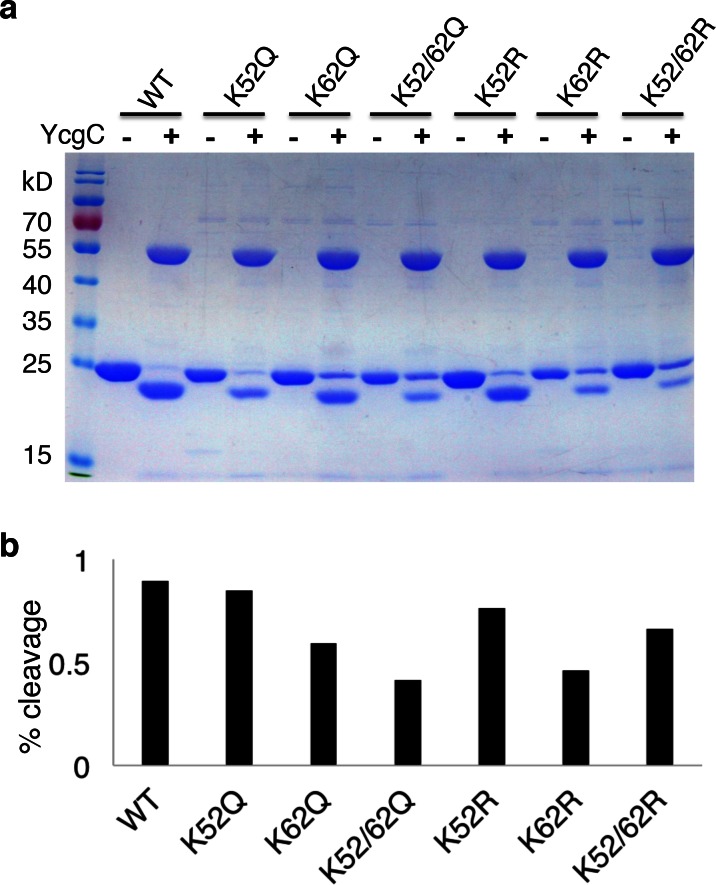
Figure 3—figure supplement 2. Lysine 62 is critical for RutR proteolysis.
Figure 3—figure supplement 3. The Km and Vmax values of YcgC were determined using RutR as a substrate.