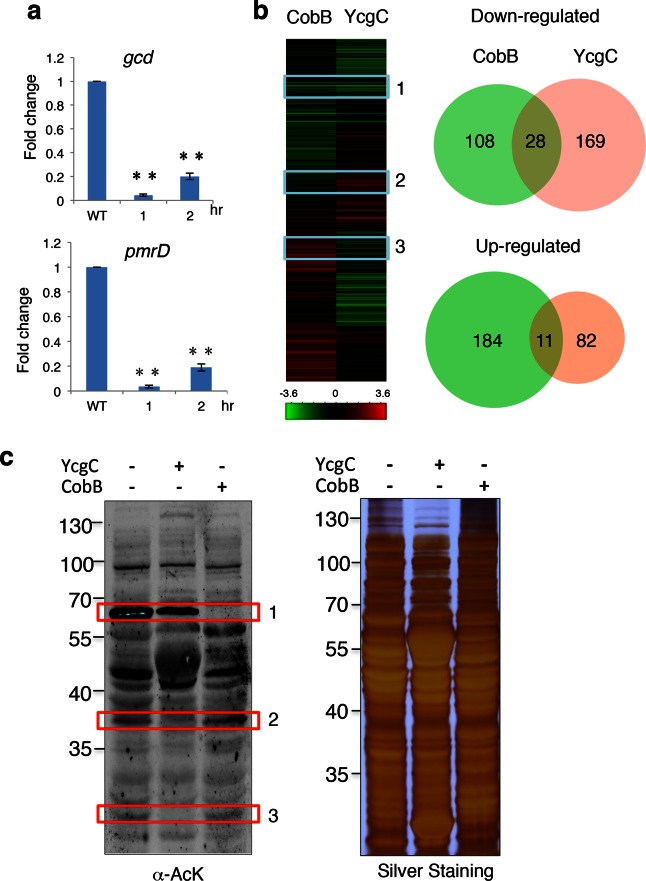
Figure 4. YcgC and CobB target distinct sets of substrates.
(a) YcgC regulates gene expression via deacetylating RutR. Expression of gcd and pmrD is significantly reduced upon RutR induction over a period of 2 hr as measured by quantitative real-time PCR. Double asterisks indicate that the observed fold changes are statistically significant, p<0.01. (b) Global gene expression analysis of ycgC- and cobB-induced cells. Clustering analysis shows clearly that impact on global transcription of induction of ycgC is distinct from that of cobB. Venn diagram showing that there is no significant overlap between genes down- and up-regulated due to CobB and YcgC induction. (c) Overexpression of YcgC affects global protein acetylation levels in E. coli. After ycgC and cobB were separately induced for 1 hr, global acetylation was detected in whole lysates of Escherichia coli using two pan α-AcK antibodies. The WT E. coli strain was also included for comparison. Boxed areas indicate regions that show obviously different staining patterns in ycgC- and cobB-induced cells. PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; WT: Wild type.