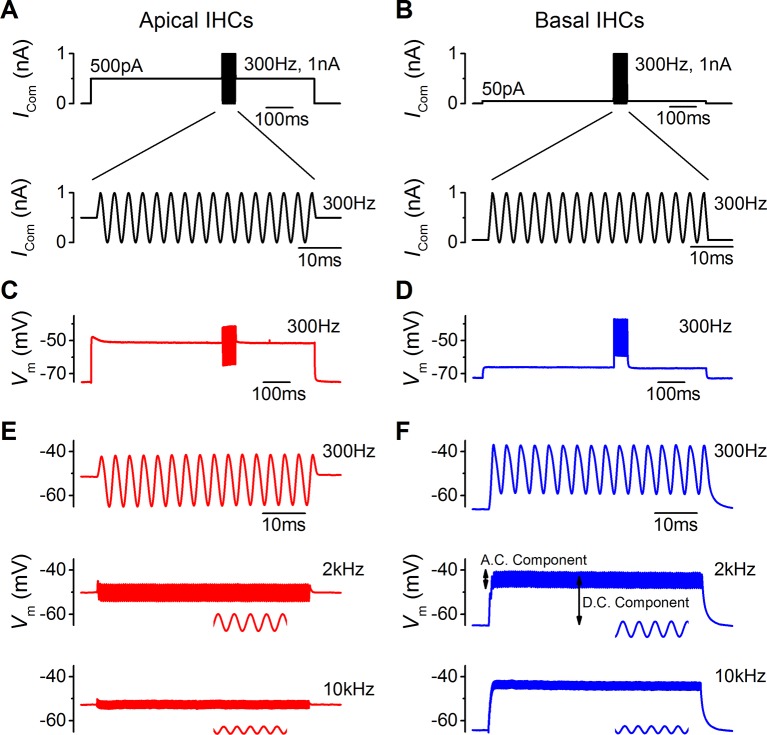
Figure 6. Sound-like stimulation of apical and basal adult gerbil inner hair cells (IHCs).
(A and B) Current clamp protocols used to mimic the in vivo sound-induced stimulation of apical (A) and basal (B) IHCs. A 300 Hz sinewave of 1 nA peak-to-peak amplitude was superimposed on a step current injection (apical: 500 pA; basal: 50 pA), which was used to depolarize lHCs to their predicted in vivo resting potential (see Results). Expanded versions of the sinewave stimulus (top) are shown below. (C and D) Average voltage responses from apical (n = 7) and basal (n = 6) IHCs in response to the whole stimulus shown in (A) and (B) (top). (E and F) Average voltage responses of apical (E) and basal (F) IHCs to a 300 Hz (top), 2 kHz (middle), and a 10 kHz (bottom) 1 nA sinewave. Only the sinewave portion of the responses is shown and the holding current levels were as in (A) and (B), respectively. An expanded portion of the 2 kHz and 10 kHz voltage responses is shown below the main trace in order to show some cycles of the sine wave. For the basal response at 2 kHz the predominantly phasic (AC) and predominantly sustained (DC) components are indicated. Apical cells showed only the AC component for 1 nA stimuli.