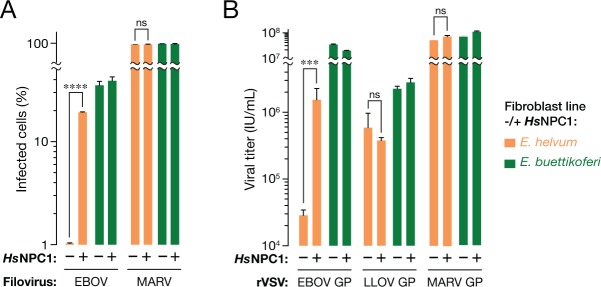
Figure 2. The NPC1-dependent entry and infection block in African straw-colored fruit bat cells is selective for EBOV.
(A) Infection of pteropodid kidney fibroblast cell lines stably expressing human NPC1 (HsNPC1) with authentic filoviruses. (B) Infection of pteropodid kidney fibroblast cell lines with recombinant VSV (rVSVs) bearing filovirus glycoproteins. IU/ml, infectious units per ml. Means ± SD (n = 3) from a representative experiment are shown in each panel. Means for infection of cell lines lacking or ectopically expressing HsNPC1 were compared by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test with Welch’s correction (***p< 0.001; ****p< 0.0001; ns, no statistical significance).
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Detection of endogenous NPC1 in pteropodid kidney fibroblast cell lines.
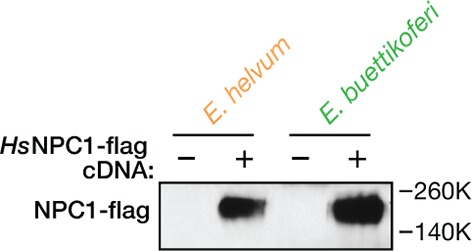
Figure 2—figure supplement 2. Ectopic expression of human NPC1 in pteropodid kidney fibroblast cell lines.