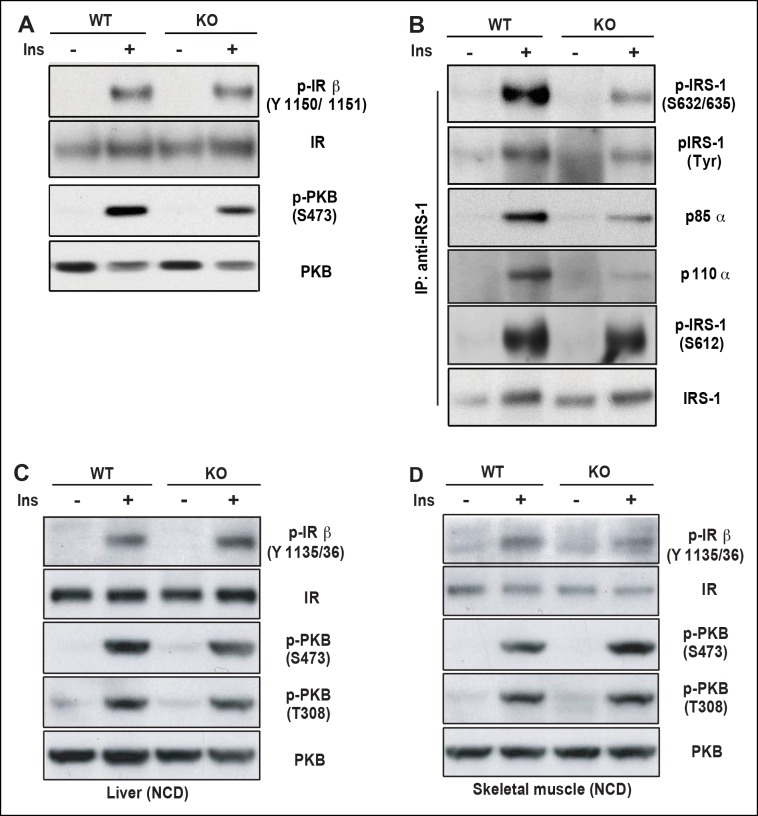
Figure 5. PDZ-RhoGEF is required for optimal IGF-1 signaling output in EWAT.
(A) IR phosphorylation and differential PKB/Akt phosphorylation in WT and PDZ-RhoGEF KO EWAT in response to insulin. (B) Serine phosphorylation of IRS1 and interaction between IRS1 and PI3K in WT and PDZ-RhoGEF KO EWAT in response to insulin. (C) IR phosphorylation and differential PKB/Akt phosphorylation in WT and PDZ-RhoGEF KO liver in response to insulin. (D) IR phosphorylation and differential PKB/Akt phosphorylation in WT and PDZ-RhoGEF KO skeletal muscle in response to insulin.