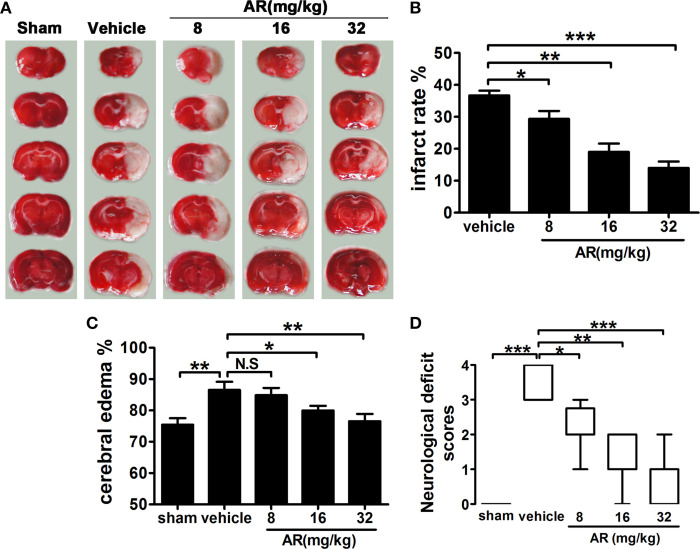
Figure 1.
The effect of AR on cerebral infarction, cerebral edema, and neurological deficit score in MCAO rats. The vehicle group and AR groups underwent MCAO while the sham group underwent the same surgical procedure without the filament inserted. After MCAO performed, rats in AR groups were intraperitoneally administrated with AR (8, 16, and 32 mg/kg) for 3 days. (A) TTC staining was applied after rats were sacrificed, and brain images were analyzed by Image J software. And infarct area percentage data indicated in (B) were calculated as infarct area/whole area. (C) Cerebral edema was calculated as formula illustrated in the methods. (D) The neurological deficit evaluation were performed at 72 h after reperfusion and analyzed with a Kruskal–Walls test followed by the Mann–Whitney U-test for multiple comparisons. Apart from neurological deficit scores, other data were presented as mean ± SD, neurological deficit scores were presented as median (n = 8). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. N.S, not significant.