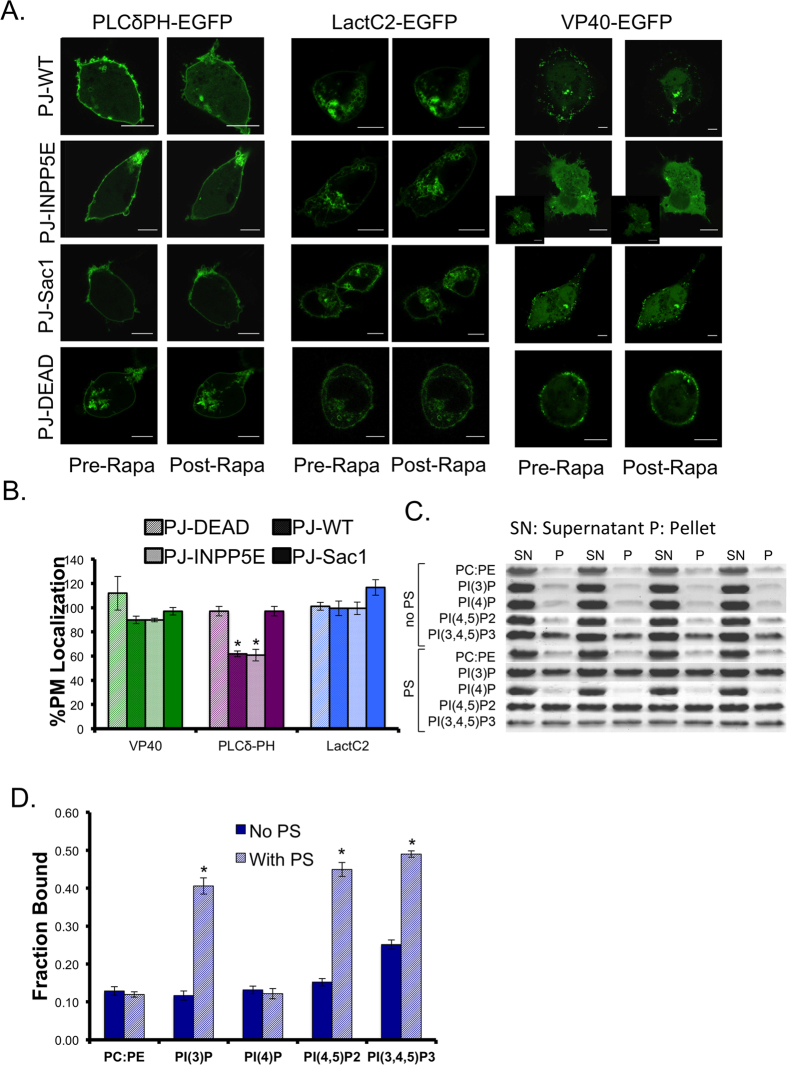
Figure 5. Real time lipid depletion and in vitro binding reveal VP40 membrane association is significantly enhanced by PI(4,5)P2.
(A) Representative images of PLCδ-PH-EGFP, LactC2-EGFP, and EGPF-VP40 pre and post rapamycin treatment with PJ-WT-FKBP-mRFP, PJ-INPP5E-FKBP-mRFP, PJ-Sac1-FKBP-mRFP, and PJ-Dead-FKBP-mRFP phosphatase constructs. PM anchor Lyn11-FRB-CFP was used in each experiment. At least 3 independent experiments were used for each condition. (B) % PM localization values were plotted for PLCδ-PH-EGFP, LactC2-EGFP, and EGFP-VP40 with depletion by PJ-WT-FKBP-mRFP, PJ-INPP5E-FKBP-mRFP, PJ-Sac1-FKBP-mRFP, and PJ-Dead-FKBP-mRFP phosphatase constructs. % PM Localization was calculated using MATLAB for each cell post rapamycin addition, normalized to pre rapamycin addition. Average values ± SEM are shown for each construct. Significant changes (p < 0.05) for each PJ-construct as compared to those with the PJ-Dead construct are marked with a star. (C) Representative SDS PAGE gel images of VP40 in the supernatant (SN) and pellet (P) with each liposome condition, 4 replicates are shown for each condition. (D) Average fraction VP40 bound to multilamellar vesicles of various composition with average values plotted ± SEM. Significant changes (p < 0.05) are marked with a star.