Figure 1.
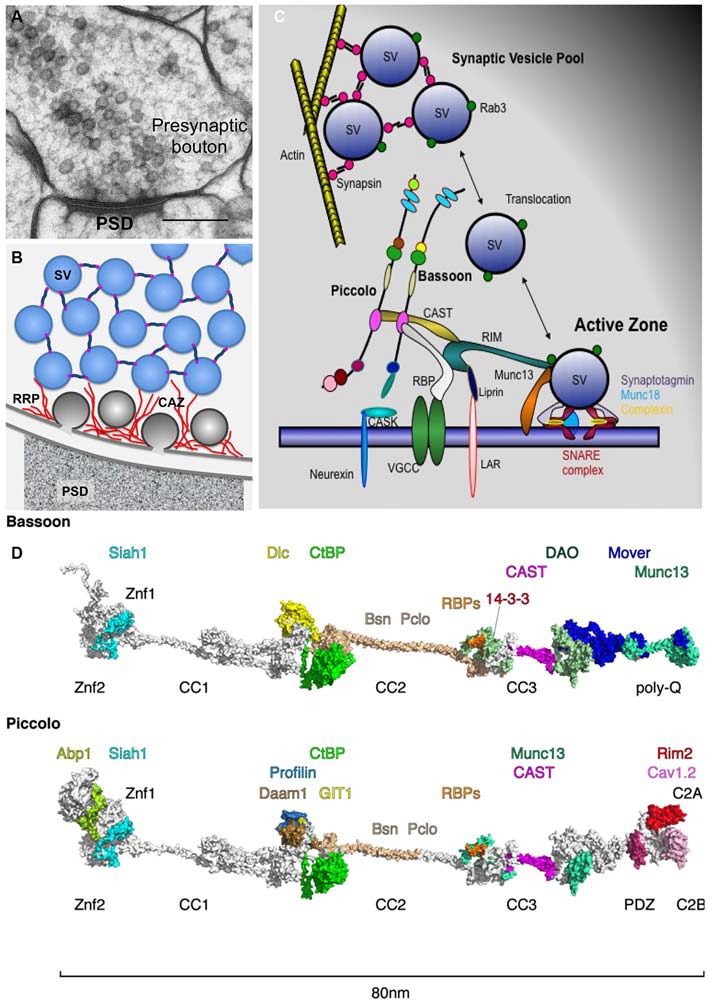
Piccolo and Bassoon at presynaptic active zones (AZ). (A) Cryo-electron micrograph of an excitatory synapse from rat brain (originally published in Rostaing et al., 2006; size bar, 200 nm). (B) Schematic organization of SVs within presynaptic boutons with SVs in the reserve pool tethered together via synapsin and those in the docked pool embedded in the CAZ (red filaments). (C) Schematic of CAZ molecules directing the clustering, translocation, docking, positional and molecular priming and fusion of SVs. (D) In-silico modeling of Bassoon and Piccolo structures with docking sites for binding partners color coded. The structures include X-ray and NMR data for Znf [protein data bank (Berman et al., 2000), PDB entry: 1ZBD], PDZ (1UJD), coiled-coil (3QH9 and Gruber and Lupas, 2003) and C2 (1RH8, 5CCG) domains. Piccolo C-terminus has been arranged similar to synaptotagmin (Zhou et al., 2015). Most of the remaining parts contain proline and glycine residues that prevent persistent folding but build compact distorted domains (Quiroz and Chilkoti, 2015), while the homologs coiled-coil helices elongate both proteins to about 80 nm. These domains were modeled ab initio using threading (Kelley and Sternberg, 2009) and BLAST routines (Sauder and Dunbrack, 2000) and visualized using PyMOL (https://www.pymol.org). For further details compare Table 1. Abbreviations: PSD, postsynaptic density; SV, synaptic vesicle; RRP, release-ready SV pool; CAZ, cytomatrix assembled at the active zone.
