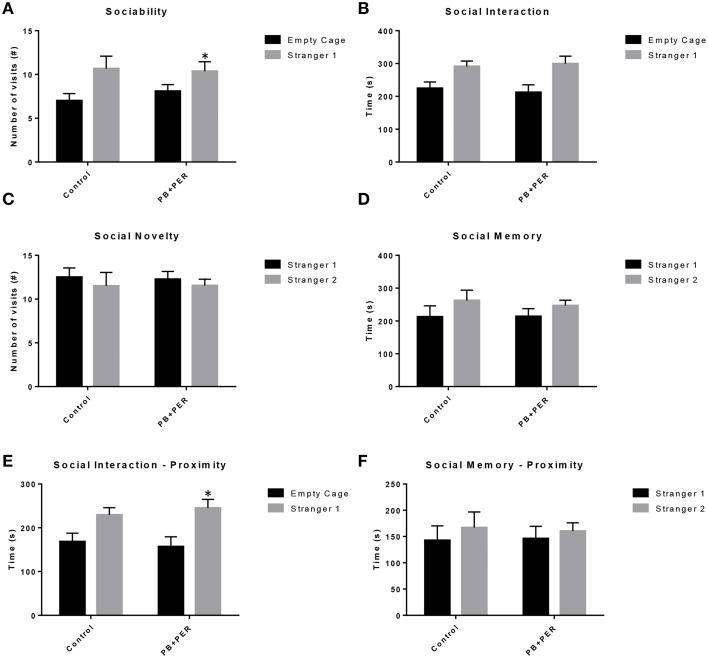
Figure 7.
Three Chamber testing revealed that PB+PER exposed mice exhibit normal sociability and social interaction behaviors, 22.5 months post exposure to GW agents. When examining (A) Sociability, the number of visits to either the empty cage or stranger 1, the control mice exhibited a slight trend toward an increased number of visits to the stranger 1 mouse as compared to the empty cage. In addition, PB+PER exposed mice demonstrated preference for the novel mouse (stranger 1) over the empty cage. When examining (B) Social Interaction, the time (s) the animals spent with either the empty cage or stranger 1, the control mice appeared to spend more time with stranger 1 as compared to the empty cage, although those differences did not reach statistical significance. Similarly, the PB+PER exposed mice continued to demonstrate a clear preference for the novel mouse (stranger 1) as compared to the empty cage. When examining (C) Social Novelty, the number of visits to either stranger 1 (familiar mouse) or stranger 2 (novel mouse), the control mice did not indicate a strong preference for one or the other, likewise, no differences in social novelty were evident when examining PB+PER exposed mice. In addition, when examining (D) Social Memory, as indicated by the time spent with either stranger 1 or stranger 2, the control mice did not demonstrate a strong preference to spend more time stranger 2 over stranger 1. Likewise, the PB+PER exposed mice did not show a strong preference for the novel mouse (stranger 2) over the familiar mouse (stranger 1). When examining (E) Social Interaction—Proximity (s), the control mice showed a trend indicating increased preference to spent more time with stranger 1 as compared to the empty cage, demonstrating normal healthy social behaviors. Likewise, the PB+PER mice showed a statistically significant preference to spent more time with stranger 1 as compared to the empty cage. When examining (F) Social Memory—Proximity (s), both the control and the PB+PER exposed mice did not show a strong preference for the novel mouse (stranger 2) over the familiar mouse (stranger 1).