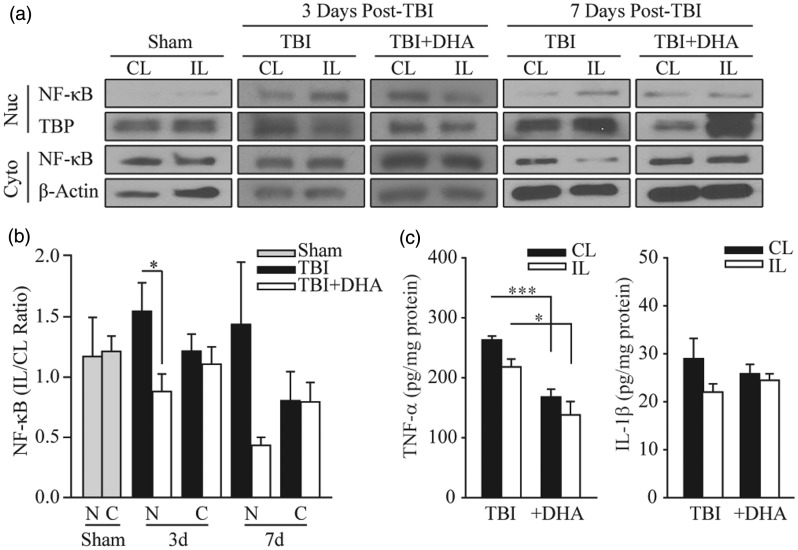
Figure 5.
DHA-treated rats exhibit reduced NF-κB translocation to the nucleus after TBI. (a) Representative immunoblots of NF-κB nuclear and cytosolic expression in the CL and IL frontal cortices of TBI and TBI + DHA animals at 3 days and 7 days post-TBI. The same blot was probed with either antibody against nuclear TATA binding protein (TBP) or against β-actin as a loading control. (b) Summary data expressed as NF-κB expression in nuclear and cytosolic fractions (IL/CL). Values are mean ± SE (sham, n = 3; 3 days post-TBI or TBI + DHA, n = 6; 7 days post-TBI or TBI + DHA, n = 3). Paired t-test used. (c) Analysis of TNF-α and IL-1β in the CL and IL cortical tissues with ELISA. Values are mean ± SE (n = 5–6). *p < .05, ***p < .001, paired t-test used.