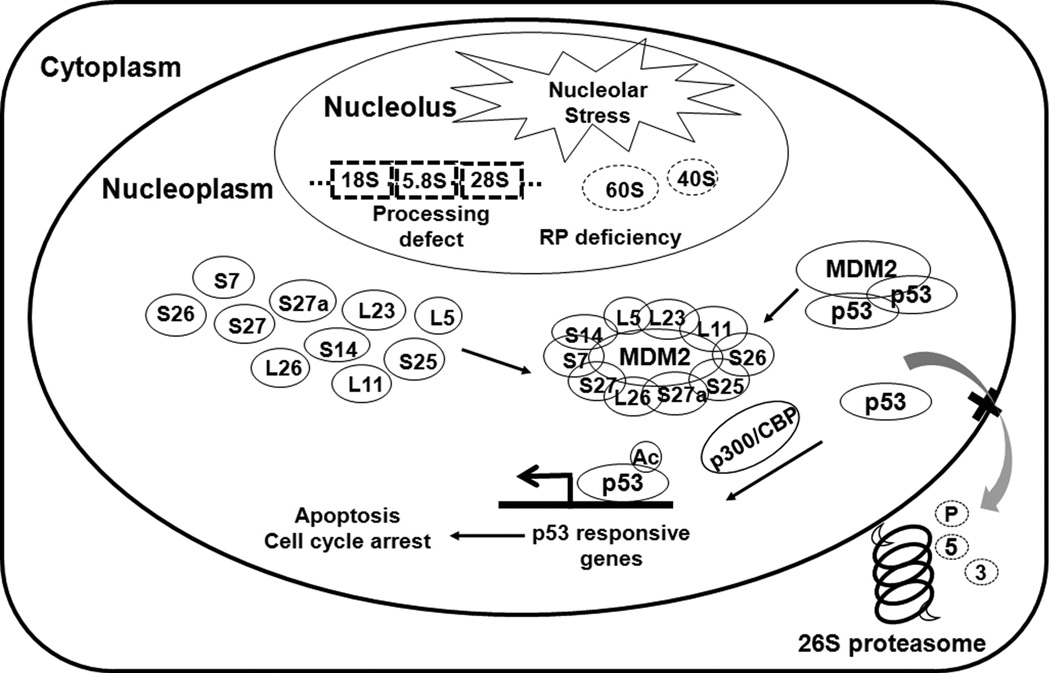
Figure 3. The RPs-MDM2-p53 interplay in nucleolar stress.
Defects in ribosome biogenesis due to impairment of rRNA synthesis or processing, nucleolar protein deficiency, or due to malfunctions trigger nucleolar stress (also called ribosomal stress). In response to nucleolar stress, a subset of RPs is released from the nucleolus to the nucleoplasm, where they bind to MDM2 and inhibit the MDM2-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of p53, leading to the stabilization and activation of p53. The RPs-MDM2-p53 interplay provides a surveillance mechanism to monitor the integrity of ribosome biogenesis and coordinate cell growth and proliferation.