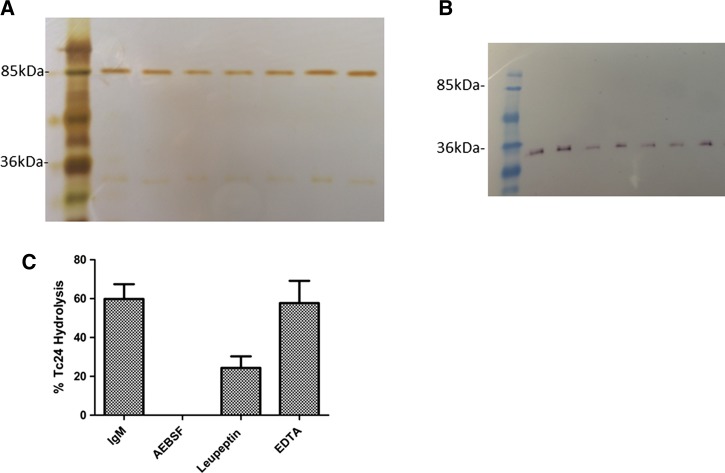
Figure 2.
IgM purity, rate, and mechanism of hydrolysis. IgM from seven mice randomly selected from respective treatment groups was subjected to sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and either (A) silver-stained or (B) transferred to nitrocellulose paper and probed with an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated rabbit anti-mouse kappa chain specific monoclonal antibody. (C) The effect of various inhibitors on IgM-mediated hydrolysis was tested by incubating 45 μg/mL IgM purified from alum-only injected mouse serum with 2.6 μM Tc24 for 48 hours at 37°C with shaking in the presence or absence of a serine protease inhibitor, AEBSF (1 mM); a cysteine protease inhibitor, leupeptin (50 μM); or a metalloprotease inhibitor, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (2 mM); and then subjected to SDS-PAGE using 15% Tris-Gly gels. Percent cleavage calculated using ImageJ.